What is a Subnet?
A subnet, short for subnetwork, is a smaller network created from a larger one. It's a logical subdivision of an IP network where devices share the same unique network address. The process of creating a subnet involves taking a large network and breaking it down into smaller networks to help organize and manage connected devices.

What is the Relationship Between Subnets and IP Addresses?
Subnets and IP addresses are closely related, as they both play crucial roles in how data is routed in a network.
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier assigned to each device on a network. It serves two main purposes: identifying the host or network interface, and providing the location of the host in the network.
A subnet, or subnetwork, is essentially a division of an IP network. The process of subnetting is used to divide a single, large network into multiple smaller networks. Each subnet in a network will have its own unique range of IP addresses.
The relationship between subnets and IP addresses can be understood through the concept of a subnet mask. A subnet mask is a number that defines how many IP addresses are contained within that subnet. It also determines which part of the IP address denotes the network and which part denotes the device.
For example, consider an IP address of 192.168.1.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Here, '192.168.1' represents the network part, and the last part '.0' represents the specific device in the network. All devices within this subnet would have an IP address that starts with '192.168.1'.
What is a Subnet Mask?
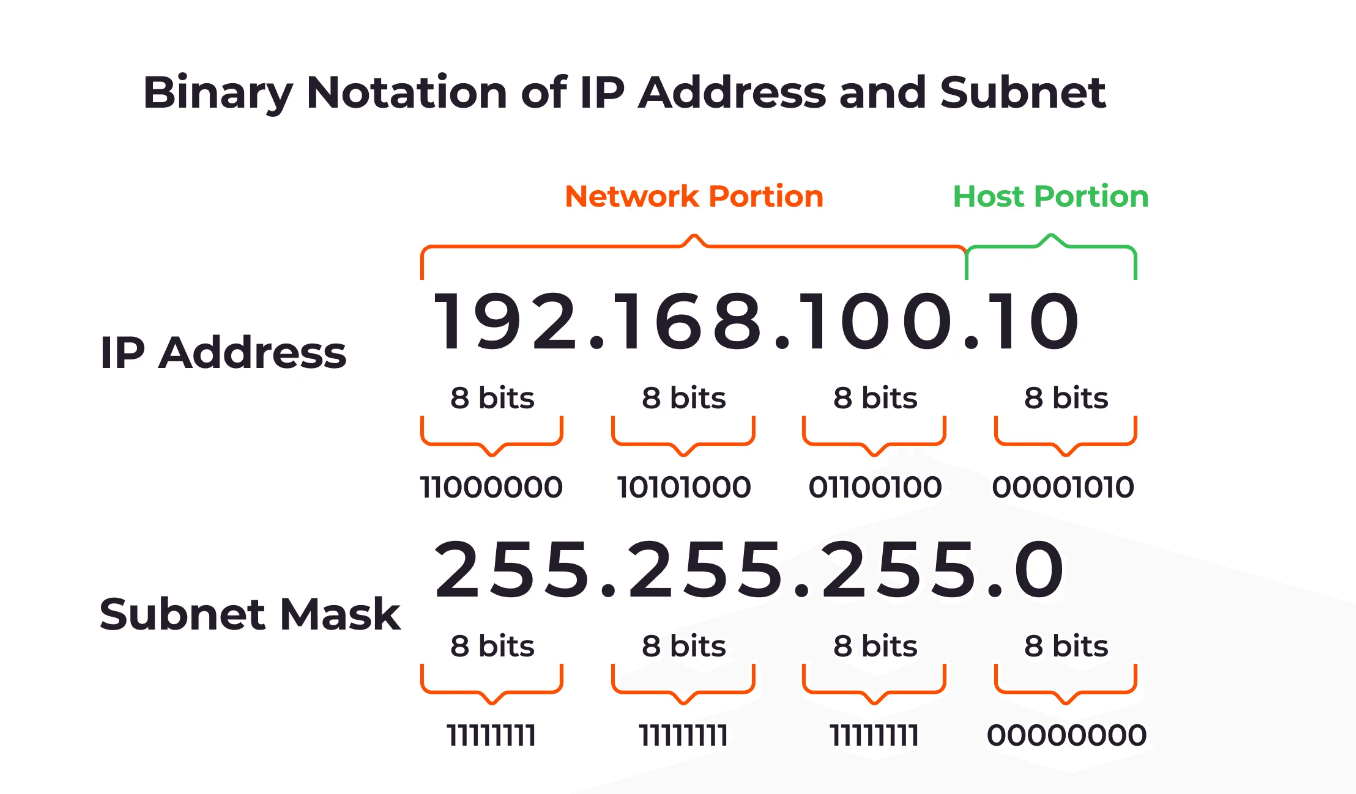
A subnet mask is a 32-bit number that masks an IP address and divides it into two parts: the network address and the host address. It's used in the subnetting process to determine how many IP addresses are available within a given network.
The subnet mask is written in the same form as an IP address (four octets), and it helps define the size of a network. The '1' bits in a subnet mask represent the network portion, while the '0' bits represent the host portion.
For example, a common subnet mask for a Class C IP address is 255.255.255.0. In binary form, this subnet mask is represented as 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000. The first three octets (each represented by 255 in decimal form) are the network address, and the last octet (represented by 0 in decimal form) is used for host addresses within that network.
The subnet mask is crucial in IP networking because it allows a device to determine whether another device is on the same network or a different one. When an IP address is combined with a subnet mask, the result identifies both the unique network and the unique device on that network.
What are Subnet Notations?
Subnet notations are used to express both the IP address and the subnet mask in a concise format. There are two common notations: slash notation (also known as CIDR notation) and subnet mask notation.
- Slash Notation / CIDR Notation: This is a compact method of expressing the IP address and subnet mask. It includes the IP address followed by a slash ('/') and the number of '1' bits in the subnet mask. For example, the IP address '192.168.1.0' with a subnet mask of '255.255.255.0' would be written as '192.168.1.0/24' in CIDR notation. The '/24' indicates that the first 24 bits are used for the network address, leaving the remaining 8 bits for host addresses.
- Subnet Mask Notation: This notation expresses the subnet mask as four octets, similar to an IP address. For example, a subnet mask that allows for 256 host addresses (254 usable) would be written as '255.255.255.0'.
Both notations provide the same information but in different formats. The choice between them often depends on the context or personal preference. CIDR notation is more compact and is commonly used in various network configurations and documentation.
Why is a Subnet Necessary?
A subnet is necessary to divide a larger network into smaller, more manageable segments. This helps in improving network performance, enhancing security, and making efficient use of IP address space. Subnetting allows for better organization and control over network traffic, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot.
What are the Benefits of Subnetting?
- Improved Network Performance and Speed: By dividing a large network into smaller subnets, network traffic can be reduced, resulting in increased network speed and performance.
- Enhanced Security: Subnets can isolate different parts of a network, limiting the impact of a security breach. If an intruder gains access to one subnet, the data and devices on other subnets remain secure.
- Efficient Use of IP Addresses: Subnetting allows for the efficient use of IP addresses. By dividing a network into subnets, organizations can use their IP address allocation more efficiently.
- Ease of Administration: Subnets make it easier to manage and troubleshoot networks. Network issues can be isolated within a subnet, making it easier to identify and resolve problems.
- Scalability: By allowing for easy expansion of the network.
- Better Traffic Control: By enabling the application of specific policies or QoS rules to different segments.
- Compliance: By helping to meet regulatory and organizational requirements for data protection and privacy.
By implementing subnets, organizations can create a more organized, secure, and efficient network environment.
Conclusion
Tencent EdgeOne provides powerful, secure and efficient network infrastructure to meet the needs of various applications and services. You can create a network and set up subnets with very simple operations. Take advantage of our exclusive offer - a Free Trial. Welcome to Contact Us for more information.

