What is VP8?
VP8 is a video compression format that was developed by On2 Technologies and released by Google in 2010. This format was created to meet the needs of online video transmission by reducing the size of video files while maintaining quality, especially in situations with limited bandwidth. Google acquired On2 Technologies and launched VP8 as part of its WebM project in 2010. The WebM project aimed to develop an open and royalty-free media format for the web to support the development of online video.
The VP8 video format offers efficient encoding and high video quality. It uses a block-based motion compensation architecture to effectively reduce video file sizes. Additionally, VP8 incorporates unique technologies and optimizations, such as a new loop filter, to enhance the handling of noise and details in videos. The advantage of VP8 is its ability to maintain high-quality video while minimizing file size, making it ideal for online video streams, particularly in low bandwidth scenarios. Being an open-source format, VP8 does not require any royalty fees, leading to widespread support and adoption within the developer community.
Despite VP8's excellent performance in many aspects, it faces competition. In 2013, Google released VP9 as the successor to VP8. VP9 improved both compression efficiency and video quality. Despite this, VP8 remains an important video encoding format, widely used in various online video services.
What is VP9?
VP9 is a video codec standard developed by Google's WebM project team to improve video compression efficiency, reduce bandwidth requirements, and maintain or enhance video quality. It was released in 2013 and is widely used in online video transmission, especially on platforms like YouTube.
VP9 uses tiered video encoding technology, allowing videos to be divided into different layers with varying quality and resolution. This enables video streams to dynamically adjust based on network conditions or device capabilities, providing a smoother playback experience. VP9 can change the size of encoding blocks based on video content complexity, ranging from 4x4 to 64x64, which helps to control compression more precisely, especially in scenes with rich detail or fast motion. It also supports 10-bit color depth, offering a broader range of colors and more delicate color gradients than VP8's 8-bit, suitable for high dynamic range (HDR) video requirements.
As an open-source project, VP9 not only reduces usage costs but also promotes its widespread adoption and continuous improvement within the developer community.
Overall, VP9, with its efficient compression technology and support for high-resolution video, provides an effective and cost-efficient solution for online video distribution and streaming media playback. With the increasing popularity of 4K and higher resolution video content, the importance of VP9 is set to grow further.

The Difference between VP8 and VP9
VP8 and VP9 are video coding and decoding standards developed by Google. They are widely used for online video transmission and are both part of the WebM project. However, VP9 has significant improvements and optimizations over VP8 in several key aspects. Below is a comparison of VP8 and VP9, covering compression efficiency, encoding strategies, resolution, compatibility, application scenarios, and parallel processing capabilities.
1. Compression Efficiency
One of the key benefits of VP9 is its significantly improved compression efficiency. VP9 achieves this through the use of more advanced prediction algorithms and block partitioning techniques. These enhancements enable VP9 to more accurately predict the value of each pixel, leading to a reduction in the amount of data that needs to be stored. Furthermore, VP9 introduces a more efficient entropy coding method, which further decreases the size of the generated files. This high compression efficiency allows VP9 to deliver higher video quality at the same bitrate, or to achieve the same quality at a lower bitrate, resulting in savings in bandwidth and storage space.
2. Encoding Strategy
The VP9 video codec offers significant improvements over VP8. These include a wider range of block sizes from 4x4 to 64x64, enabling better compression optimization for different parts of the video. VP9 also incorporates more advanced inter-frame prediction techniques and enhanced support for intra-frame prediction modes to improve compression efficiency, especially for handling various types of motion and details in the video content.
3. Resolution
VP9's support for high-resolution video is a significant advantage. It can effectively handle video content up to 4K and even 8K. This is particularly important for streaming service providers who need to transmit high-resolution video without sacrificing quality. VP9's capabilities make it an important tool for the future development of video technology, especially as high-definition video becomes increasingly common.
4. Compatibility
Despite its numerous technical advantages, VP9's compatibility issues cannot be ignored. Because VP9 is newer and more complex, some older devices and software may not support videos encoded with VP9. This could limit its use on older devices. However, as technology evolves, more and more devices and browsers are beginning to natively support VP9.
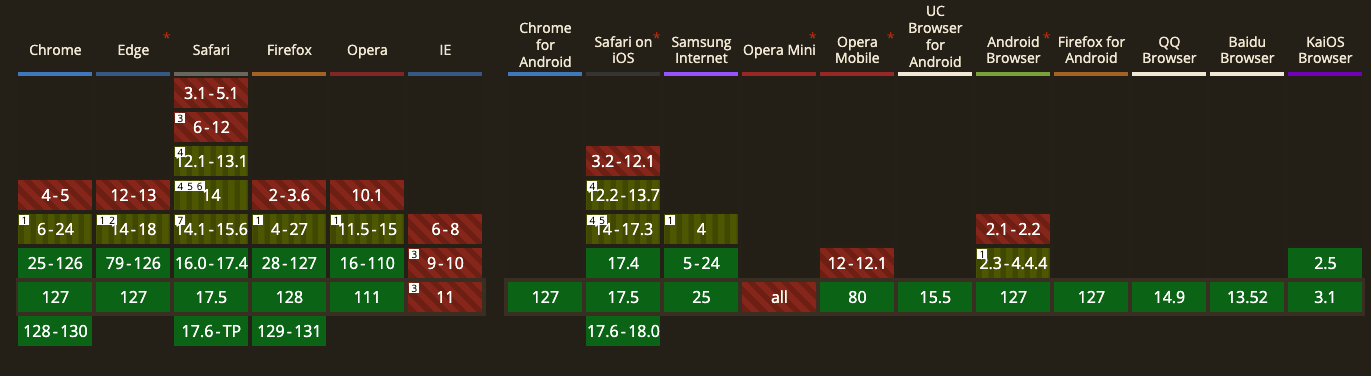
WebM browser support
5. Application Scenarios
Because of its outstanding compression efficiency and support for high-resolution videos, VP9 is especially well-suited for scenarios that demand both high video quality and efficient data transmission, such as online video streaming services. Major video platforms like YouTube have embraced VP9 to deliver higher-quality video content. On the other hand, VP8 is more suitable for applications that do not require high encoding complexity, like video conferencing and lower-resolution video streams.
6. Parallel Processing Capability
VP9 includes enhancements in parallel processing, which supports better intra-frame parallel encoding and tile-based encoding. This allows it to make more efficient use of the capabilities of modern multi-core processors. These improvements are crucial for speeding up the video encoding process and reducing latency, especially in real-time video communication and large-scale video processing.
In summary, VP9 outperforms VP8 in terms of compression efficiency, resolution support, and parallel processing capabilities, although it may slightly lag in compatibility. With ongoing technological advancements and broader support, VP9 is expected to become even more widely adopted.
VP8 vs VP9: Which to Choose?
When choosing between VP8 and VP9, it's important to consider technical details, cost-benefit analysis, and long-term technical support and development trends. Here is a detailed analysis of these factors:
1. Technical Details and Features
VP9 incorporates a range of advanced technologies. These include more complex block partitioning (with block sizes ranging from 4x4 to 64x64) and more efficient entropy coding methods. These advancements give VP9 a significant edge in compression efficiency, enabling it to deliver higher video quality at lower bitrates. Additionally, VP9 supports more advanced inter-frame and intra-frame prediction technologies, which can better handle motion and detail changes in videos, thereby reducing the amount of data generated during encoding.
In contrast, VP8, although not as technologically advanced as VP9, offers faster encoding and decoding speeds due to its simplicity. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where large volumes of video data need to be processed quickly, such as in real-time video conferencing. Furthermore, VP8 has broader hardware support, which means that VP8 videos can be played directly on more devices without additional processing.
2. Cost-Benefit Analysis
Although VP9 offers higher compression efficiency, its encoding and decoding processes are typically more resource-intensive. This may lead to higher hardware requirements and more energy consumption. Before implementing VP9, it is necessary to assess whether there are sufficient computing resources to support its efficient encoding and decoding processes, especially in mobile devices or other resource-limited environments.
In the long run, as high-resolution video content such as 4K and 8K becomes more common, VP9 or its subsequent technologies (like AV1) may become more economical choices because they can significantly reduce data transmission and storage needs without sacrificing video quality.
3. Technical Support and Development Trends
As a newer technology, VP9 has garnered support from several major tech companies, including Google. These companies not only extensively utilize VP9 in their products (such as YouTube), but also advocate for its widespread acceptance and compatibility in the industry. Over time, we can anticipate increased native support for VP9 in more devices and browsers, further enhancing its usability.
In contrast, although VP8 is currently more widely supported, being an older technology means its development and update speed may not keep pace with that of VP9. As the market demands higher video quality and greater compression efficiency, VP8 might gradually be supplanted by newer encoding standards.
In summary, the choice between VP8 and VP9 should be based on specific application needs, target device compatibility, and encoding efficiency requirements. If the focus of the project is on compatibility and low latency, VP8 might be the more suitable choice. However, for applications seeking high video quality and data efficiency, especially in resource-rich environments, VP9 offers more advantages. As technology evolves and new devices become prevalent, VP9's support will continue to expand, making it the mainstream choice for future video encoding.
Conclusion
If you need to ensure broad device compatibility, VP8 is a good choice, especially when you do not need extremely high-resolution video. For scenarios that require high-resolution video support (such as 4K or higher) and want to take advantage of higher compression efficiency, VP9 is a more suitable choice, especially if you can accept the higher demands on encoding resources.
In summary, the choice of codec depends on your specific needs, including budget, compatibility with target platforms, video quality requirements, and whether you need to deal with royalty fees.
If your platform experiences high video streaming traffic and covers a broad user base, you might need to deploy these videos across multiple global nodes, allowing every user to access and play the videos quickly and from the nearest location. Tencent EdgeOne is a globally leading product that integrates security and acceleration. We have now launched a Free Trial, welcome to Contact Us for more information.

