Understanding CDN Security: How It Works and Why It Matters
In today’s digital landscape, where online presence is paramount, ensuring the security of your website and its content is more critical than ever. One of the most effective ways to enhance website performance and security is through a Content Delivery Network (CDN). This blog will delve into CDN security, how it works, best practices for securing your CDN, its key benefits, and the potential risks associated with CDN security.
What is CDN Security?
Content Delivery Network (CDN) security refers to the measures and protocols implemented to protect the data and content delivered through a CDN. A CDN is a network of distributed servers that work together to deliver web content to users based on their geographic location. By caching content closer to users, CDNs improve load times and reduce latency. However, as with any technology, CDNs can be vulnerable to various security threats, including Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, data breaches, and content tampering.
CDN security encompasses a range of strategies and technologies designed to safeguard the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of the content delivered through the network. This includes encryption, access controls, DDoS mitigation, and more. By implementing robust CDN security measures, businesses can protect their online assets and ensure a seamless experience for their users.
How CDN Security Works?
CDN security operates through a combination of technologies and practices designed to protect data as it travels across the network. Here’s a breakdown of how CDN security works:
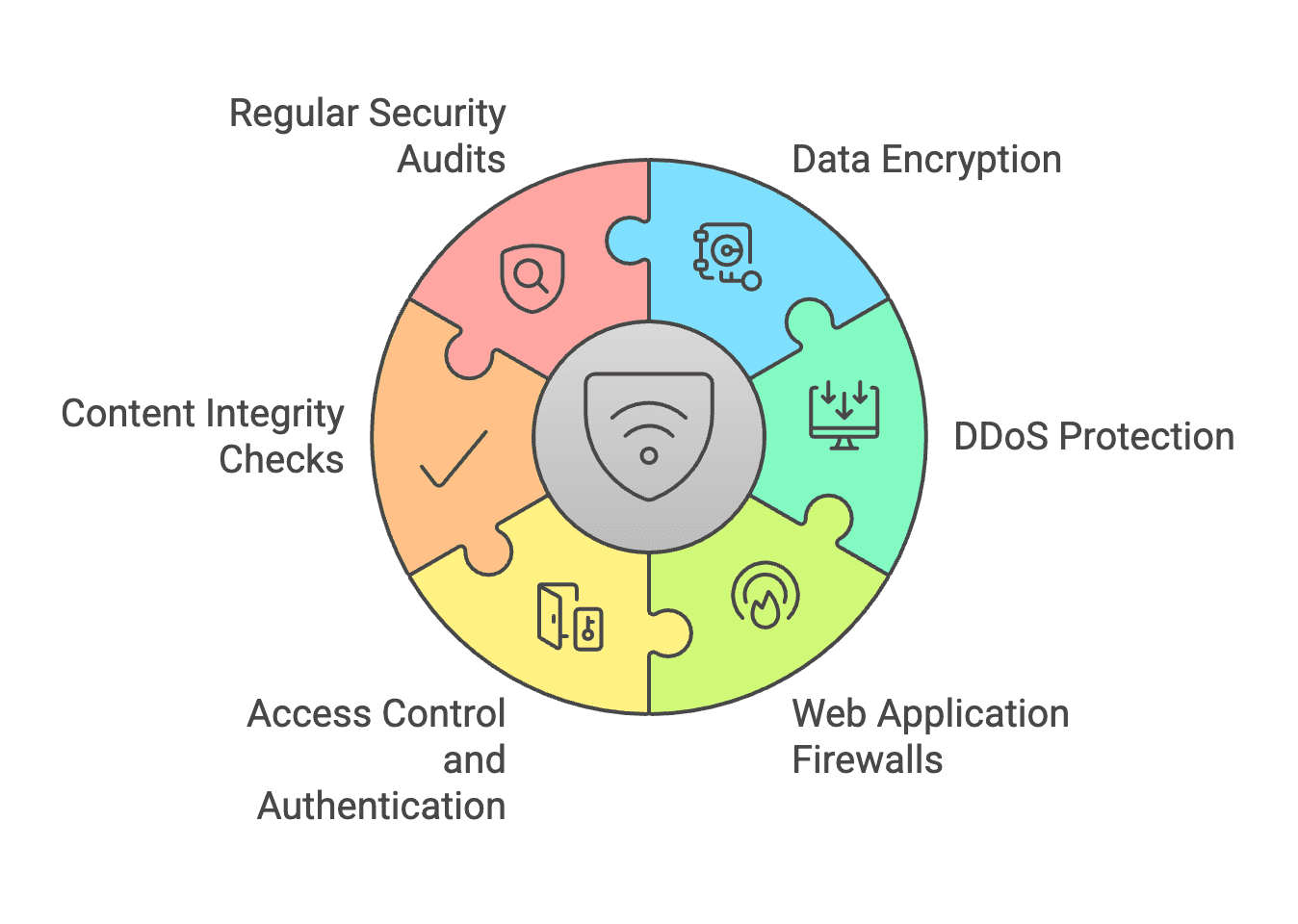
1. Data Encryption
One of the primary methods of securing data in transit is through encryption. CDNs often use SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to encrypt data between the user’s browser and the CDN server. This ensures that sensitive information, such as login credentials and payment details, is protected from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
2. DDoS Protection
DDoS attacks aim to overwhelm a server with traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. CDNs are equipped with DDoS mitigation tools that can detect and filter out malicious traffic before it reaches the origin server. By distributing traffic across multiple servers, CDNs can absorb and mitigate the impact of DDoS attacks, ensuring that legitimate users can still access the content.
3. Web Application Firewalls (WAF)
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) is a critical component of CDN security. It monitors and filters HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet. WAFs protect against common web vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and other application-layer attacks. By analyzing incoming traffic and blocking malicious requests, WAFs help maintain the integrity of web applications.
4. Access Control and Authentication
CDNs can implement access control measures to restrict who can access certain content or resources. This includes using token-based authentication, IP whitelisting, and user authentication protocols. By ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive content, CDNs help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
5. Content Integrity Checks
To ensure that the content delivered through the CDN has not been tampered with, integrity checks can be performed. This involves using checksums or hash functions to verify that the content remains unchanged during transmission. If any discrepancies are detected, the CDN can take appropriate action, such as alerting administrators or blocking the compromised content.
6. Regular Security Audits and Updates
CDN providers often conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that their systems are up to date with the latest security patches. This proactive approach helps mitigate potential risks and ensures that the CDN remains secure against emerging threats.
Key Benefits of a Secure CDN
Implementing a secure CDN offers several benefits for businesses and website owners:
1. Improved Performance
A secure CDN not only enhances security but also improves website performance. By caching content closer to users, CDNs reduce latency and load times, leading to a better user experience.
2. Enhanced Security
With robust security measures in place, a secure CDN protects against various threats, including DDoS attacks, data breaches, and content tampering. This helps safeguard sensitive information and maintain the integrity of your website.
3. Increased Availability
CDNs distribute traffic across multiple servers, ensuring that your website remains available even during traffic spikes or attacks. This redundancy enhances the reliability of your online presence.
4. SEO Benefits
Search engines prioritize secure websites in their rankings. By implementing HTTPS and securing your CDN, you can improve your website’s SEO performance and visibility.
5. Cost-Effective Security
Using a CDN can be a cost-effective way to enhance security. Instead of investing in expensive hardware and software solutions, businesses can leverage the security features offered by CDN providers.
Understanding CDN Security Risks
While CDNs offer numerous security benefits, they are not without risks. Understanding these risks is essential for implementing effective security measures:
1. Data Breaches
If not properly secured, CDNs can be vulnerable to data breaches. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data stored on CDN servers.
2. Misconfiguration
Improperly configured CDNs can expose sensitive content or create security loopholes. It’s crucial to follow best practices during the setup and configuration process to minimize risks.
3. Third-Party Dependencies
Using a CDN means relying on a third-party provider for security. If the CDN provider experiences a security incident, it can impact your website’s security and availability.
4. DDoS Attacks
While CDNs can mitigate DDoS attacks, they are not immune to them. Sophisticated attacks can still overwhelm CDN servers, leading to service disruptions.
5. Content Spoofing
Attackers may attempt to spoof content delivered through a CDN, leading to misinformation or brand damage. Implementing content integrity checks can help mitigate this risk.
Securing Your CDN: Best Practices
Implementing best practices for CDN (Content Delivery Network) security is essential to protect your website and its content from various threats. Here are some key CDN security best practices to consider:
1. Choose a Reputable CDN Provider
- Research Providers: Select a CDN provider with a strong reputation for security. Look for features like DDoS protection, Web Application Firewalls (WAF), and SSL/TLS support.
- Security Certifications: Check if the provider has relevant security certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2) that demonstrate their commitment to security.
2. Enable HTTPS
- SSL/TLS Encryption: Always use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit. Ensure that your CDN supports SSL/TLS and that you have valid SSL certificates installed.
- Automatic HTTPS Rewrites: Enable automatic HTTPS rewrites to ensure that all resources are loaded securely.
3. Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- Traffic Filtering: Use a WAF to monitor and filter HTTP traffic between your web application and the internet. Configure it to block common web vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Custom Rules: Set up custom rules to address specific threats relevant to your application.
4. Regularly Update Security Protocols
- Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest security threats and best practices. Regularly update your security protocols, including encryption standards and access controls.
- Patch Management: Ensure that all software and systems are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
5. Monitor Traffic and Logs
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuously monitor traffic patterns and server logs for unusual activity. Implement alerting mechanisms to notify you of potential security incidents.
- Anomaly Detection: Use tools that can detect anomalies in traffic patterns, which may indicate a security threat.
6. Conduct Security Audits
- Regular Assessments: Perform regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of your CDN security measures. Identify vulnerabilities and take corrective actions to strengthen your security posture.
- Penetration Testing: Consider conducting penetration tests to simulate attacks and identify weaknesses in your security setup.
7. Implement Access Control and Authentication
- Restrict Access: Use access control measures to restrict who can access certain content or resources. Implement IP whitelisting and user authentication protocols.
- Token-Based Authentication: Use token-based authentication for APIs and sensitive resources to ensure that only authorized users can access them.
8. Use Content Integrity Checks
- Checksum Verification: Implement integrity checks using checksums or hash functions to verify that the content delivered through the CDN has not been tampered with.
- Alerting Mechanisms: Set up alerts for any discrepancies detected during integrity checks.
9. Educate Your Team
- Security Training: Conduct training sessions for your team to raise awareness about potential threats and the importance of maintaining security protocols.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and communicate incident response plans to ensure that your team knows how to respond to security incidents effectively.
10. Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Regular Backups: Ensure that you have regular backups of your website and content. Store backups in a secure location separate from your primary servers.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: Develop a disaster recovery plan that outlines steps to restore services in the event of a security breach or data loss.
11. Limit the Use of Third-Party Scripts
- Review Third-Party Content: Be cautious when using third-party scripts or resources, as they can introduce vulnerabilities. Regularly review and audit these scripts for security.
- Subresource Integrity (SRI): Use Subresource Integrity (SRI) attributes for third-party scripts to ensure that the files have not been tampered with.
12. Implement Rate Limiting
- Control Traffic: Use rate limiting to control the number of requests a user can make to your server within a specific timeframe. This helps mitigate DDoS attacks and brute-force attempts.
13. Utilize Geo-Blocking
- Restrict Access: If your business operates in specific regions, consider implementing geo-blocking to restrict access from countries or regions that are not relevant to your audience.
14. Regularly Review CDN Configuration
- Configuration Management: Regularly review and update your CDN configuration to ensure that it aligns with your security policies and best practices.
- Remove Unused Resources: Periodically audit your CDN to remove any unused or outdated resources that could pose security risks.
How Tencent EdgeOne Optimizes Your Network Services?
EdgeOne leverages over 3,200 edge nodes across 100+ countries and regions to deliver lightning-fast content globally. Through advanced GSLB (Global Server Load Balancing) and intelligent routing optimization, it ensures optimal performance by automatically directing users to the nearest edge node, significantly reducing latency and improving content delivery efficiency for both static and dynamic content.
EdgeOne integrates comprehensive security features directly at the edge, providing enterprise-grade protection against various cyber threats. With global cleaning centers offering 15Tbps+ total protection capacity and advanced AI-powered security engines, it effectively defends against DDoS attacks, malicious bots, SQL injections, and other web vulnerabilities while ensuring legitimate traffic flows smoothly.
By combining both acceleration and security capabilities at the edge, EdgeOne delivers a unified solution that optimizes performance while maintaining robust protection for your web services. This integration eliminates the need for separate CDN and security solutions, simplifying management and reducing operational complexity.
Ready to experience enterprise-grade acceleration and security? Start your free plan with EdgeOne today and get 1TB of data transfer included.
FAQs About CDN Security
Q1: What security features does a CDN typically provide?
A1: Modern CDNs offer DDoS protection, WAF (Web Application Firewall), bot management, and SSL/TLS encryption to protect websites from various cyber threats.
Q2: How does CDN DDoS protection work?
A2: CDNs use distributed networks of servers to absorb and filter malicious traffic before it reaches your origin server, effectively mitigating DDoS attacks.
Q3: Can CDNs help prevent data breaches?
A3: Yes, CDNs provide security features like SSL/TLS encryption and access control rules to protect sensitive data during transmission and storage.
Q4: What is WAF in CDN security?
A4: A Web Application Firewall (WAF) monitors and filters HTTP traffic between a web application and the Internet, blocking malicious requests and common web exploits.
Q5: How does CDN rate limiting protect websites?
A5: Rate limiting restricts the number of requests from a single IP address within a specific timeframe, helping prevent brute force attacks and abuse.
Q6: Are CDNs compliant with security regulations?
A6: Leading CDN providers maintain compliance with major security standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, and ISO 27001 to ensure data protection and privacy.

