In today's digital age, website speed and performance are critical for user experience, making Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) an essential component of internet infrastructure. A CDN is a sophisticated network of strategically placed proxy servers and data centers around the world, designed to deliver content to users quickly and reliably.
CDNs emerged in the late 1990s as a response to increasing internet performance challenges and have since developed into powerful systems that form the backbone of modern web content delivery. They manage a wide range of digital content, from basic web elements like text and images to complex applications, streaming media, and dynamic social media platforms. By positioning content closer to end users within a distributed network architecture, CDNs not only enhance performance but also ensure consistent availability and improved security.
Whether you are streaming your favorite show, shopping online, or browsing social media, you are likely interacting with a CDN, often without even realizing it. These invisible yet vital networks now account for up to 70% of all internet traffic, making them fundamental to our experience of the modern web.
What is a CDN?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is an advanced system of servers located in various geographical regions, aimed at speeding up the delivery of web content. This distributed infrastructure acts as a link between content providers (the origin servers) and end users. It optimizes the content delivery process by utilizing efficient caching methods and smart routing technologies.
Core Architecture and Components
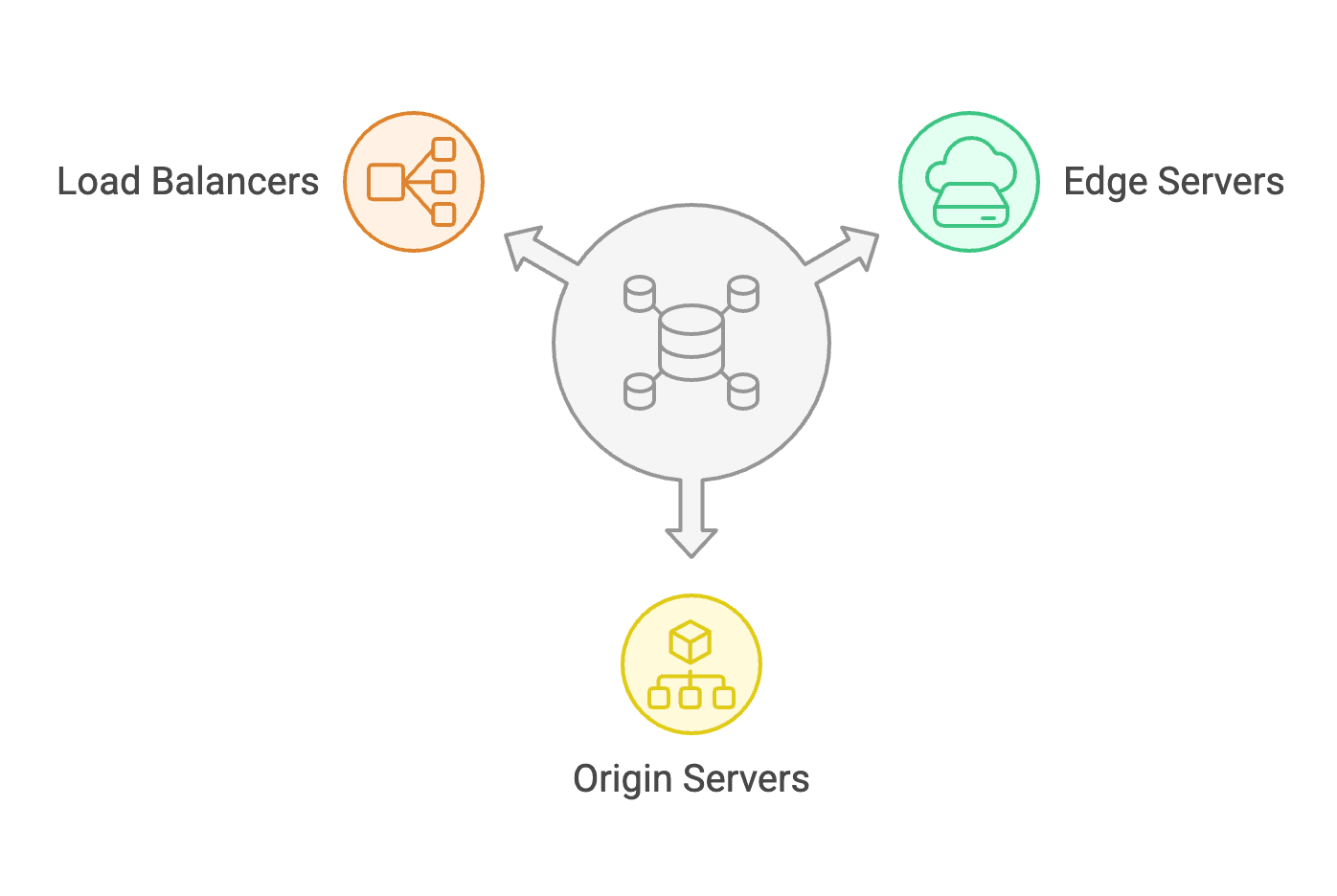
The core CDN architecture is composed of several key components that work together to ensure efficient content distribution and optimal user experience.
- Edge Servers (Points of Presence - PoPs): Strategically located around the world, these servers cache content closer to end-users. They act as the primary distribution points for nearby users, significantly reducing latency and improving load times.
- Origin Servers: These servers host the original, authoritative content and maintain the master copies of all website assets. They handle requests that cannot be served from the cache, ensuring that the most up-to-date content is always available.
- Load Balancers: Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed. They ensure optimal resource utilization and maintain server performance by efficiently managing the distribution of user requests.
How Does a CDN Work?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) transforms web content delivery through a global network of servers strategically located around the world. This distributed architecture significantly reduces latency, ensures consistent availability, and optimizes performance for end-users. The operation of a CDN involves three key processes: Initial Request and Caching, Geographic Distribution and Routing, and Content Management.
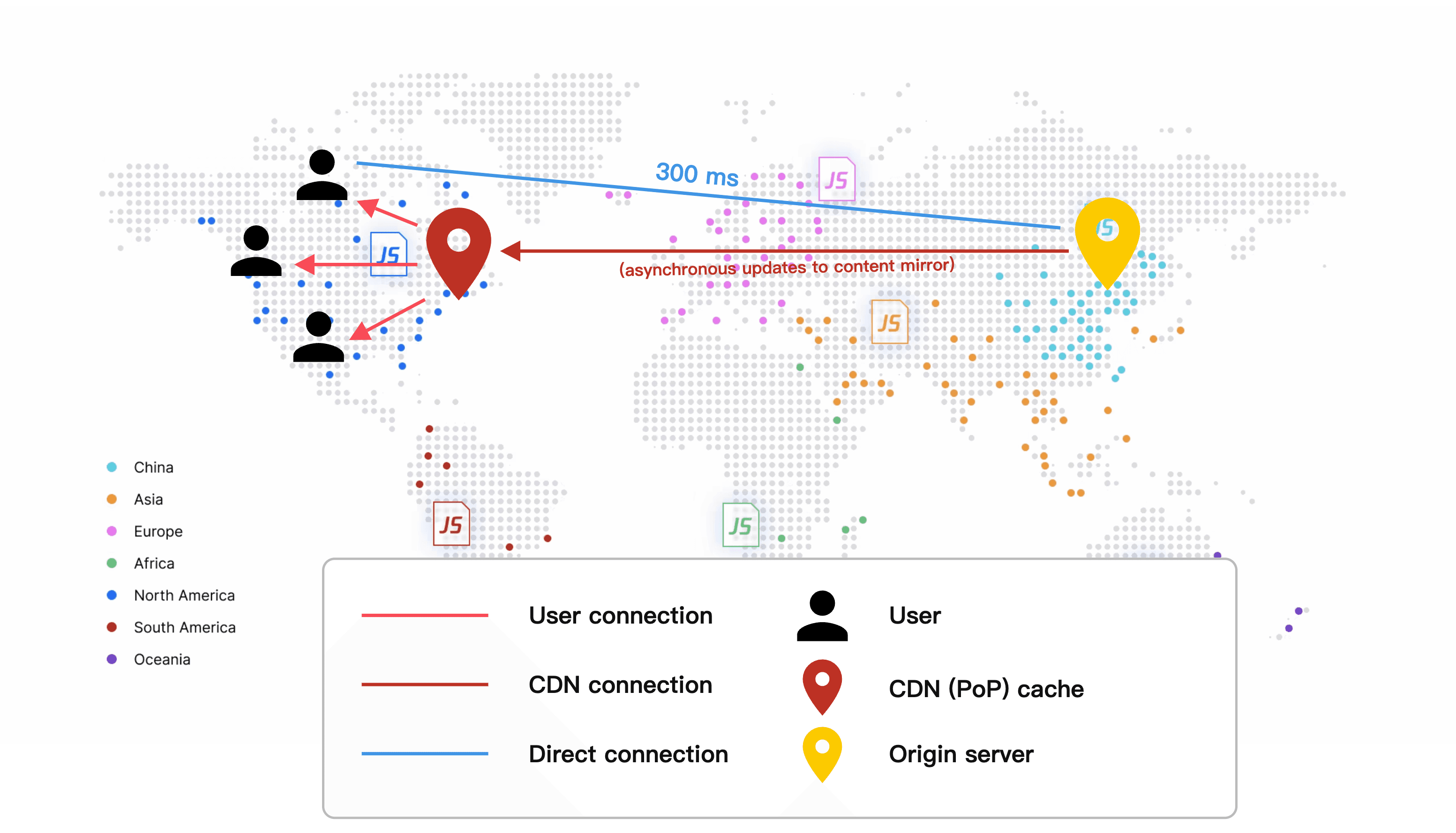
1. Initial Request and Caching
When a user requests content, the CDN employs a smart caching mechanism. It first checks for the content on the nearest edge server. If the content is not found locally, the CDN retrieves it from the origin server while simultaneously caching it on edge servers based on predefined rules. This intelligent caching system allows subsequent requests to be served directly from the local cache, dramatically improving response times and alleviating the load on the origin server. This process turns what could be a long-distance data journey into a local content delivery operation.
2. Geographic Distribution and Routing
The CDN uses advanced DNS-based request routing to link users with the best edge servers. This system utilizes Anycast routing technology, which allows multiple servers to share a single IP address while directing users to the most efficient server based on their location. The network continuously conducts real-time health checks to ensure service reliability, and dynamic path optimization algorithms adjust routing paths based on current network conditions, traffic patterns, and server performance metrics.
3. Content Management
Modern CDNs implement robust content management systems that extend beyond basic caching. The network features intelligent cache refresh mechanisms that proactively update content based on changes from the origin server. Sophisticated content versioning and purging capabilities provide precise control over cache management, ensuring that content remains accurate and up-to-date. The origin shield protection acts as a barrier between edge servers and the origin, preventing traffic surges from overwhelming the source. Advanced compression and optimization techniques further enhance delivery efficiency by automatically adjusting content format and size according to user devices and network conditions.
Through this coordinated system, CDNs deliver a seamless content experience. The network's distributed architecture, alongside intelligent routing and sophisticated content management, ensures that users receive content from the optimal source with minimal latency. This approach not only accelerates content delivery but also offers robust scalability and reliability, making CDNs a vital component of modern web infrastructure. The system's ability to adapt automatically to changing conditions and optimize delivery paths guarantees consistently high-performance content delivery on a global scale.
Key Benefits of CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a transformative technology that significantly enhances web service delivery across several critical areas. Through its distributed server architecture, CDNs provide remarkable improvements in performance, cost management, reliability, and global accessibility.
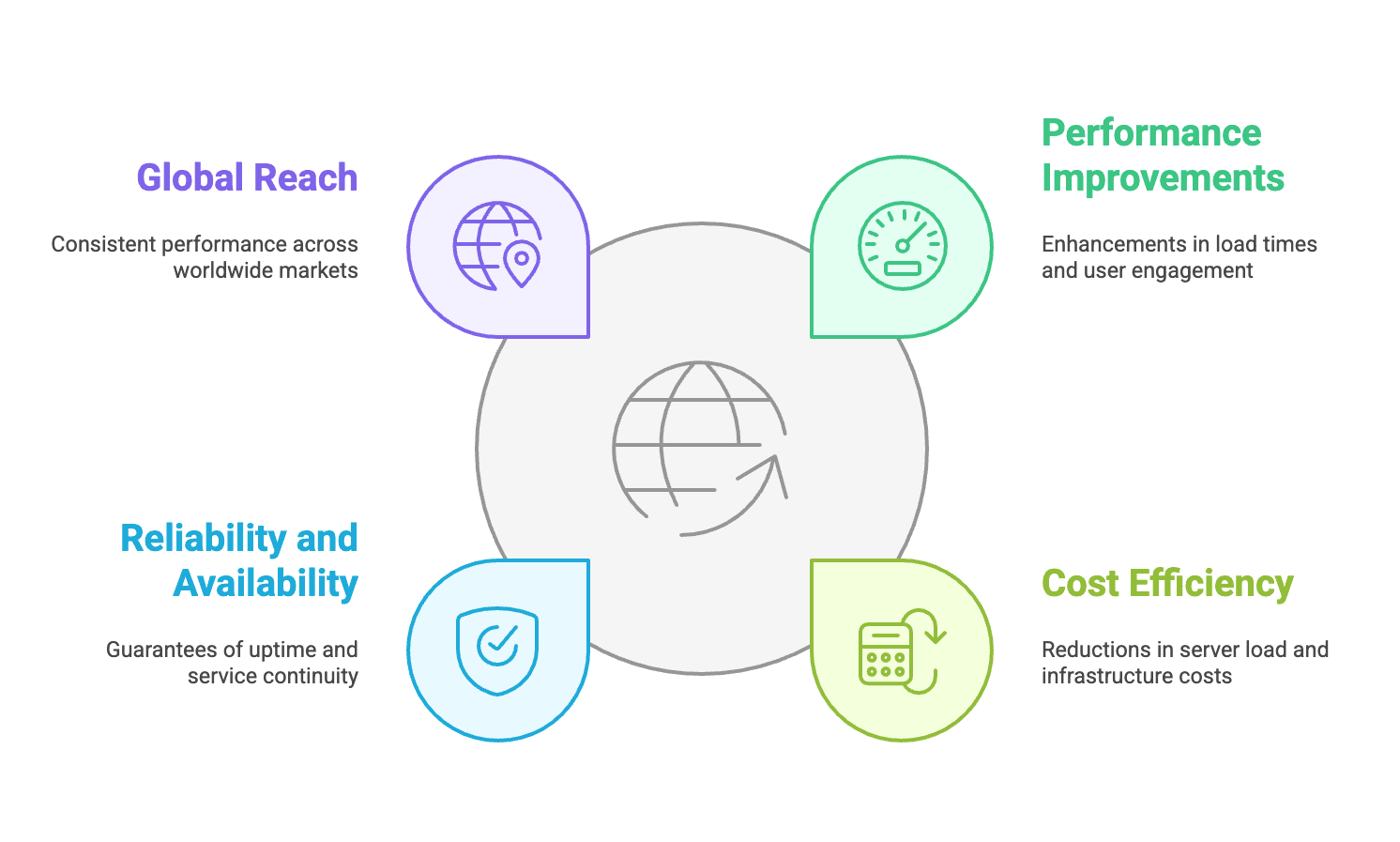
1. Performance Improvements
CDNs greatly enhance website performance using advanced caching and routing mechanisms, achieving impressive reductions of 20-80% in page load times. This improvement is a result of strategically placed edge servers and intelligent content distribution algorithms. Key performance metrics optimized include:
- Time to First Byte (TTFB): Significantly reduced through edge caching and optimized routing.
- Time to Interactive (TTI): Enhanced by sophisticated content prioritization and loading strategies.
- Core Web Vitals: Substantially improved through comprehensive performance optimizations.
- Network Latency: Minimized by the smart geographic distribution of content.
These performance enhancements contribute directly to improved search engine rankings, lower bounce rates, and higher user engagement metrics.
2. Cost Efficiency
The economic advantages of implementing a CDN are substantial and quantifiable. Organizations typically experience:
- A 60-70% reduction in origin server load through intelligent traffic distribution.
- Significant bandwidth optimization via advanced caching strategies.
- Lower infrastructure costs due to efficient resource utilization.
- Scalable pricing models that align with actual usage patterns.
These cost savings not only include direct financial benefits but also improved resource allocation and reduced maintenance needs. This comprehensive approach to cost management makes CDNs a compelling solution for organizations of all sizes.
3. Reliability and Availability
CDNs set a new standard for service reliability through sophisticated redundancy and failover systems:
- Guaranteed uptime of 99.9% or higher thanks to the distributed architecture.
- Robust automatic failover mechanisms with real-time health monitoring.
- Advanced management of load spikes through intelligent traffic distribution.
- Geographic redundancy that ensures continuous service availability.
This multi-layered approach to reliability ensures consistent performance even during challenging conditions, such as traffic surges or regional network issues. Such resilience is essential for maintaining continuous service delivery and ensuring user satisfaction.
4. Global Reach
CDNs excel in providing consistent, high-quality performance across global markets through:
- Strategically positioned edge locations in key markets worldwide.
- Advanced edge computing capabilities for localized processing.
- Multi-CDN architecture that supports optimal content delivery.
- Regional performance optimization based on local network conditions.
This global infrastructure enables organizations to maintain consistent service quality no matter the user's location while adhering to regional compliance requirements and performance standards.
The comprehensive benefits of CDNs extend beyond just content delivery, forming a foundation for reliable, efficient, and scalable web services. As digital experiences become increasingly vital to business success, CDNs continue to evolve, adopting new technologies and capabilities to meet emerging challenges and opportunities in content delivery and application performance.
Real-World Applications of CDNs
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and reliability of various online services across multiple industries. By utilizing a network of distributed servers, CDNs ensure that content is delivered quickly and efficiently to users around the globe.
- E-commerce: CDNs greatly improve the online shopping experience by ensuring that product pages and images load quickly. They also support secure payment processing and facilitate smooth shopping cart operations, which are vital for reducing cart abandonment rates.
- Media Streaming: CDNs enable buffer-free video streaming by distributing content through servers that are geographically closer to users. They support both live and on-demand streaming while automatically adjusting video quality based on the user's connection speed.
- Gaming: Gaming platforms rely on CDNs to quickly deliver game assets and updates to players worldwide. They provide low-latency connections for multiplayer games, enabling real-time synchronization between players.
- Enterprise Applications: CDNs enhance the performance of Software as a Service (SaaS) applications and APIs for business users around the globe. They offer secure access to corporate resources while maintaining fast loading times for dynamic content.
Overall, CDNs are essential for optimizing performance, reliability, and security across various online services in different industries. In e-commerce, media streaming, gaming, and enterprise applications, CDNs improve user experience by ensuring quick content delivery, reducing latency, and providing robust security.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have become essential to modern web infrastructure, fundamentally changing how content is delivered across the internet. By distributing content through a global network of servers, utilizing intelligent routing, and offering robust content management capabilities, CDNs ensure that businesses of all sizes can deliver content faster, more reliably, and securely.
EdgeOne represents the next evolution in content delivery and security solutions. By combining enterprise-grade CDN capabilities with advanced security features, EdgeOne provides:
- Global Coverage: Strategic Points of Presence (PoPs) to ensure optimal performance worldwide
- Integrated Security: Built-in DDoS protection, Web Application Firewall (WAF), and bot management
- Intelligent Routing: Advanced traffic management and load balancing
- Simple Management: A unified dashboard for performance and security controls
Start your journey with EdgeOne today. Experience how our integrated CDN and security solution can accelerate your content delivery while protecting your digital assets. Sign up for a free trial and join the thousands of businesses already benefiting from EdgeOne's powerful capabilities.

