What is M3U8 and What is M3U Playlist? How to Open and Convert It?

M3U8, as a common video format, is widely used in online video playback, live streaming, and other streaming media services. Compared to traditional video formats like MP4, M3U8 brings more efficient video transmission, flexible adaptation, and enhanced content protection. If you are looking to transcode, distribute, and host M3U8 videos, you might want to consider our services.
The M3U (Moving Picture Experts Group Audio Layer 3 Uniform Resource Locator) file format is not essentially an audio or video file. It cannot read network resource audio or video in offline mode. It is a playlist file for audio and video files and is a plain text file.
The Unicode version of M3U is M3U8, which uses UTF-8-encoded characters. M3U8 files are the basis for the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) format originally developed by Apple to stream video and radio to iOS devices, and which is now a popular format for adaptive streaming in general.
The specific calculations and explanations are detailed in the M3U8 section of the English version of Wikipedia. As we can see, the m3u8 file is a part of the HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol.
What is HLS?
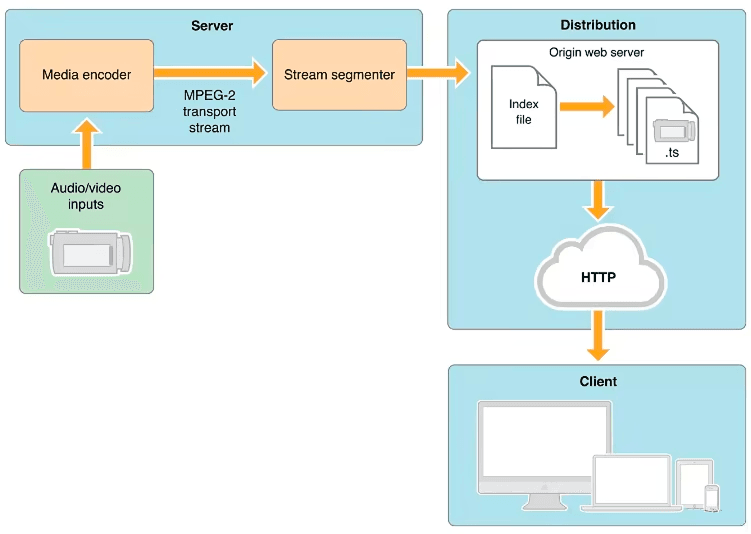
HLS is a media streaming protocol based on HTTP developed by Apple Inc. It was primarily designed to address the issues of transmitting and playing online video streams.
Compared to traditional streaming media technologies such as RTSP protocol (there are three types of streaming media protocols: RTMP, RTSP, and HTTP Live Streaming), HLS has the advantage that once the segmentation is completed, no additional specialized software is required for distribution, and a regular web server can be used, which reduces the technical requirements for servers. For widely used CDN services, it greatly reduces the configuration requirements of CDN edge servers and can use any existing CDN.
For non-real-time video, if you want to jump in a long video using a single MP4 format video file and the HTTP protocol, you need a proxy server that supports HTTP range requests to obtain a part of the large file. Not all proxy servers support this well. HTTP Live Streaming only needs to download the corresponding TS segment based on the timeline in the m3u playlist file, without HTTP range requests, which requires less of a proxy server because all proxy servers support efficient caching of small files.
In addition, using TS for streaming media packaging has another advantage, which is that there is no need to load the index before playing, greatly reducing the initial loading delay and improving the user experience.
Furthermore, the biggest advantage of HTTP Live Streaming is adaptive bitrate streaming. The client automatically selects video streams of different bitrates based on the network conditions, using high bitrates when conditions permit and low bitrates when the network is busy, and automatically switches between the two. This is very helpful for ensuring smooth playback in unstable mobile device network conditions.
What is the M3U8 and M3U Playlist?
The m3u8 file is essentially a m3u playlist, which can be a media playlist or a master playlist. However, regardless of the type of playlist, the text used inside is encoded in UTF-8.
When the m3u8 file is used as a media playlist, it records a series of media segment resources that can be played in sequence to display the complete multimedia resource. Its format is as follows:
#EXTM3U
#EXT-X-TARGETDURATION:10
#EXTINF:9.009,
http://media.example.com/first.ts
#EXTINF:9.009,
http://media.example.com/second.ts
#EXTINF:3.003,
http://media.example.com/third.tsFor on-demand playback, the client only needs to download the segment resources in order and play them one by one. However, for live streaming, the client needs to periodically request the m3u8 file to check if there are new segment data that need to be downloaded and played.
When the m3u8 file is used as a master playlist, it provides a list of variant streams for the same media resource. Its format is as follows:
#EXTM3U
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=150000,RESOLUTION=416x234,CODECS="avc1.42e00a,mp4a.40.2"
http://example.com/low/index.m3u8
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=240000,RESOLUTION=416x234,CODECS="avc1.42e00a,mp4a.40.2"
http://example.com/lo_mid/index.m3u8
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=440000,RESOLUTION=416x234,CODECS="avc1.42e00a,mp4a.40.2"
http://example.com/hi_mid/index.m3u8
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=640000,RESOLUTION=640x360,CODECS="avc1.42e00a,mp4a.40.2"
http://example.com/high/index.m3u8
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=64000,CODECS="mp4a.40.5"
http://example.com/audio/index.m3u8The variant stream resources specify multiple media playlists with different bitrates and formats. Additionally, the variant stream resources can also provide different versions of the content, such as audio files in different languages or video files shot from different angles. Clients can select the appropriate bitrate resources based on different network conditions, and it is recommended to select the appropriate content based on user preferences.
To learn more about the m3u playlist and the HLS protocol, you can refer to the following links:
Adding Alternate Media to a Playlist
M3U8 File Format
The m3u8 file format mainly includes three aspects:
M3U Playlist
The content of the m3u playlist (m3u8 file) must strictly comply with the requirements of the defined specification. The following are some of the main conditions that need to be followed:
- The m3u8 file must be encoded in UTF-8 and cannot use Byte Order Mark (BOM) byte order. It cannot contain utf-8 control characters (U+0000 ~ U_001F and U+007F ~ u+009F).
- Each line of the m3u8 file must be either a URI, an empty line, or a string starting with #. No white-space characters are allowed except for explicitly declared elements.
- Strings starting with # in the m3u8 file are either comments or tags. Tags start with #EXT and are case-sensitive.
Attribute Lists
Some specific tags have values in the form of attribute lists. The attribute list following the tag is separated into multiple sets of attribute/value pairs without spaces, using a comma as the separator.
The syntax format of the attribute/value pair is as follows:
AttributeName=AttributeValueThe AttributeName is an unquoted string composed of [A..Z], [0..9], and -. Therefore, AttributeName can only use uppercase letters and cannot use lowercase letters. There should be no spaces between AttributeName and =, and similarly, there should be no spaces between = and AttributeValue.
Tags
Tags are used to specify the global parameters of the m3u8 file or some information about the segment files/media playlists that follow it.
Tags can be divided into five types: Basic Tags, Media Segment Tags, Media Playlist Tags, Master Playlist Tags, and Playlist Tags. Their specific contents are shown below:
- Basic Tags:
- #EXTM3U
- #EXT-X-VERSION
- #EXT-X-ALLOW-CACHE
- #EXT-X-MEDIA-SEQUENCE
- #EXT-X-TARGETDURATION
- Media Segment Tags:
- #EXTINF
- #EXT-X-BYTERANGE
- #EXT-X-DISCONTINUITY
- #EXT-X-KEY
- #EXT-X-MAP
- #EXT-X-PROGRAM-DATE-TIME
- #EXT-X-DATERANGE
- Media Playlist Tags:
- #EXT-X-TITLE
- #EXT-X-PLAYLIST-TYPE
- #EXT-X-MEDIA
- #EXT-X-STREAM-INF
- #EXT-X-I-FRAME-STREAM-INF
- #EXT-X-ENDLIST
- Master Playlist Tags:
- #EXT-X-MEDIA
- #EXT-X-STREAM-INF
- #EXT-X-I-FRAME-STREAM-INF
- #EXT-X-SESSION-DATA
- #EXT-X-SESSION-KEY
- Playlist Tags:
- #EXT-X-DISCONTINUITY-SEQUENCE
- #EXT-X-ENDLIST
- #EXT-X-INDEPENDENT-SEGMENTS
- #EXT-X-START
- #EXT-X-VERSION
How to Open M3U8 Files?
M3U8 files are playlists containing references to media files. They can be opened and played using media players that support the M3U8 format. Here are the steps to open M3U8 files:
- VLC media player
- Windows Media Player
- QuickTime Player
- KMPlayer
- RealNetworks RealPlayer
- EdgeOne Online M3U8 Player
We provide a free online M3U8 Player that supports WebRTC, FLV, and HLS live streaming, as well as on-demand playback in HLS, DASH, FLV, and MP4 formats for your convenience. Feel free to use it.
M3U8 files are typically used for streaming media content over the internet. The media files referenced in the playlist may not be stored locally on your computer, but rather on a remote server. Therefore, a stable internet connection is required to play the media files smoothly.
How to Create an M3U8 File?
Creating an M3U8 file involves generating a playlist file that references media files, typically for streaming purposes. M3U8 is a UTF-8 encoded version of the M3U playlist file format, commonly used for HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create an M3U8 file:
Step 1: Gather Your Media Files
Ensure you have all the media files (e.g., video segments) you want to include in your playlist. These files should be accessible via a web server if you plan to stream them over the internet.
Step 2: Create the M3U8 File
1. Open a Text Editor: Use a text editor like Notepad (Windows), TextEdit (Mac), or any code editor (e.g., VSCode, Sublime Text).
2. Start with the Header: The first line of an M3U8 file should be #EXTM3U, which indicates that the file is an extended M3U playlist.
3. Add Media Information: For each media file, you need to add metadata and the file path. The basic format is:
- #EXTINF:<duration>,<title>: This line provides the duration (in seconds) and an optional title for the media segment.
- <file_path_or_URL>: This line specifies the path or URL to the media file.
Example:
#EXTM3U
#EXTINF:10,Segment 1
http://example.com/media/segment1.ts
#EXTINF:10,Segment 2
http://example.com/media/segment2.ts
#EXTINF:10,Segment 3
http://example.com/media/segment3.ts4. Save the File: Save the file with a .m3u8 extension, ensuring it is encoded in UTF-8.
Step 3: Advanced Features (Optional)
- Add Bandwidth and Resolution Information: For adaptive streaming, you can specify different quality levels using #EXT-X-STREAM-INF.
#EXTM3U
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=1280000,RESOLUTION=640x360
http://example.com/low/index.m3u8
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=2560000,RESOLUTION=1280x720
http://example.com/mid/index.m3u8
#EXT-X-STREAM-INF:BANDWIDTH=5120000,RESOLUTION=1920x1080
http://example.com/high/index.m3u8- Use #EXT-X-ENDLIST: If your playlist is not a live stream and has a definite end, you can add #EXT-X-ENDLIST at the end of the file.
Step 4: Test Your M3U8 File
- Local Testing: Use a media player that supports M3U8 files, like VLC, to test your playlist locally.
- Web Testing: If streaming online, ensure your web server is configured correctly to serve the media files and test using a compatible player or browser.
By following these steps, you can create a functional M3U8 file for streaming media content.
How to Download M3U8 Videos?
Downloading M3U8 videos involves fetching the video segments referenced in the M3U8 playlist file and combining them into a single video file. Here are several methods to download M3U8 videos:
Method 1: Using FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a powerful multimedia framework that can handle various video and audio formats. It can be used to download and convert M3U8 streams into a single video file.
1. Install FFmpeg
- Windows: Download the FFmpeg executable from the official website and add it to your system PATH.
- Mac: Use Homebrew to install FFmpeg:
brew install ffmpeg. - Linux: Use your package manager, e.g.,
sudo apt-get install ffmpegfor Debian-based systems.
2. Download the M3U8 Video
Open a terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
ffmpeg -i "http://example.com/path/to/playlist.m3u8" -c copy output.mp4Replace http://example.com/path/to/playlist.m3u8 with the URL of the M3U8 file and output.mp4 with your desired output file name.
Method 2: Using a Browser Extension
There are several browser extensions available that can help you download M3U8 videos directly from your web browser.
1. Install a Browser Extension
- Chrome: Extensions like "Video DownloadHelper" or "HLS Downloader".
- Firefox: Extensions like "Video DownloadHelper" or "HLS Downloader".
2. Download the Video
- Navigate to the webpage containing the M3U8 video.
- Use the extension to detect and download the video. Follow the extension's instructions to save the video to your computer.
Method 3: Using Online Services
There are online services that can download M3U8 videos for you. However, these services may have limitations and privacy concerns.
1. Find an Online M3U8 Downloader
Search for online M3U8 downloaders, such as "M3U8 Downloader" or "HLS Downloader".
2. Download the Video
- Paste the URL of the M3U8 file into the online downloader.
- Follow the instructions to download the video.
Method 4: Using Command-Line Tools
There are command-line tools specifically designed for downloading M3U8 videos.
1. Install a Tool
- youtube-dl: A popular command-line program that can download videos from various websites, including those using M3U8. Follow the instructions on the official website to install the youtube-dl.
2. Download the Video
Open a terminal or command prompt and run the following command:
youtube-dl "http://example.com/path/to/playlist.m3u8"Replace http://example.com/path/to/playlist.m3u8 with the URL of the M3U8 file.
Important Considerations
- Legal Issues: Ensure you have the right to download the content. Downloading copyrighted material without permission is illegal.
- Quality: The quality of the downloaded video depends on the quality of the segments referenced in the M3U8 file.
- Dependencies: Some methods may require additional software or dependencies to be installed on your system.
By following these methods, you can download M3U8 videos and save them as a single video file on your computer.
M3U8 vs MP4: Which is Better?
M3U8 files are playlists containing references to media files, while MP4 is a video file format. The choice between M3U8 and MP4 depends on your specific needs and use cases, as they serve different purposes in the realm of video streaming and playback. Here’s a comparison to help you understand their differences and determine which is better for your situation:
M3U8
M3U8 is a playlist format used primarily for HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), a protocol developed by Apple.
Usage
M3U8 contains links to media files (usually segmented video files) that can be streamed over the internet. It's commonly used for live streaming and adaptive bitrate streaming, which adjusts video quality based on the viewer's network conditions.
Advantages
- Adaptive Streaming: Automatically adjusts the video quality for optimal playback depending on the user's internet speed.
- Live Streaming: Ideal for broadcasting live events.
- Segmented Files: Allows for efficient streaming of large video files by breaking them into smaller segments.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Supported on many devices and browsers.
Disadvantages
- Not a Standalone File: An M3U8 file itself does not contain video data; it references other files, which means it requires a compatible player to stream the content.
- Increased Complexity: Setting up HLS streaming can be more complex compared to serving a single MP4 file.
MP4
MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14) is a digital multimedia format used for storing video and audio, as well as subtitles and images.
Usage
Commonly used for downloading and playing videos on various devices and platforms, including computers, smartphones, and media players.
Advantages
- Widespread Compatibility: Supported by most media players and devices, making it easy to share and view.
- Standalone File: Contains all video and audio data in one file, simplifying distribution.
- Quality Control: Offers good compression without significant loss of quality, making it suitable for high-definition video.
Disadvantages
- No Adaptive Streaming: Does not support automatic quality adjustments based on network conditions.
- File Size: Larger file sizes compared to segmented streams, which can be an issue for slower connections or limited storage.
Summary
- Choose M3U8 if: You are looking to implement live streaming or need adaptive bitrate streaming for varying internet speeds. It’s ideal for web applications, online broadcasts, and situations where users may experience fluctuating bandwidth.
- Choose MP4 if: You want a simple, widely-compatible format for sharing and playing back video files. It’s best suited for downloadable content, offline viewing, and scenarios where adaptive streaming is not necessary.
Ultimately, the "better" option depends on your specific requirements—whether you prioritize streaming capabilities and adaptability (M3U8) or simplicity and compatibility (MP4).
How to Convert M3U8 to MP4?
To convert M3U8 to MP4, you need to download the media files referenced in the playlist and then use a video converter to convert them to MP4 format.
- Download the media files referenced in the M3U8 playlist. You can use a video downloader tool such as Video DownloadHelper, VLC media player, or IDM (Internet Download Manager) to download the media files.
- Once the media files are downloaded, use a video converter tool to convert them to MP4 format. There are many video converter tools available online, such as HandBrake, Any Video Converter, and Freemake Video Converter.
- Open the video converter tool and select the media files you want to convert. Choose the MP4 format as the output format.
- Customize the video settings such as resolution, bitrate, and frame rate if necessary.
- Start the conversion process and wait for it to complete.
- Once the conversion is complete, you will have an MP4 video file that you can play on any media player that supports MP4 format.
Converting M3U8 to MP4 may result in a loss of quality, depending on the video converter tool and settings used.
How to Rewrite M3U8 Files?
Tencent Edge Functions provides a serverless code execution environment for the edge nodes of Tencent EdgeOne. Thanks to the programmable capabilities of EdgeOne edge functions, developers can process M3U8 media files at edge nodes and dynamically modify and inject content. Rewriting and processing M3U8 files can help developers achieve richer and more flexible streaming media application scenarios. Here are some common scenarios:
- Customized playlist: Developers may need to choose different media streams based on users' network conditions, device performance, or geographic location.
- Content security and access control: To protect copyrighted content, developers may need to process M3U8 files to implement encryption, add access tokens, and other features.
- Ad insertion: Inserting ads in streaming media content is a common business model. Developers can modify M3U8 files to insert ad segments at specific times during video playback.
In the blog post "How to Rewrite M3U8 Files?", we introduced how to dynamically modify the content of M3U8 files using Tencent Edge Functions. For a practical example of M3U8 rewriting, access control, and more code implementations, we invite you to explore our GitHub repository.
Conclusion
In conclusion, M3U8 is a powerful and flexible file format for streaming multimedia content. It has become increasingly popular due to its adaptability and ease of use. If you have more extensive needs related to video asset management, such as swift uploading, transcoding, storage, and accelerated playback, EdgeOne VOD is the perfect solution.
Tencent EdgeOne VOD (Video on Demand) offers an extensive suite of features such as cloud video storage, video transcoding, and video playback acceleration, ensuring a quick, flexible, and high-quality video delivery. This allows you to focus on your core business, pick and choose services as per your needs, and swiftly adapt to market changes. We also offer a free plan for you to get started. Click here to begin your journey with us.
FAQs
1. What is an M3U8 file?
An M3U8 file is a playlist file format used for HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). It is a text file encoded in UTF-8 that contains a list of URLs or file paths to media segments, typically video or audio files.
2. How does M3U8 work?
M3U8 files work by listing the locations of media segments that a media player can download and play sequentially. This allows for adaptive bitrate streaming, where the quality of the video can adjust based on the viewer's internet connection.
3. What is the difference between M3U and M3U8?
The primary difference is the encoding. M3U files are typically encoded in ANSI or other character sets, while M3U8 files are specifically encoded in UTF-8, which supports a wider range of characters.
4. How can I open an M3U8 file?
You can open an M3U8 file with various media players that support HLS, such as:
- VLC Media Player
- Apple QuickTime Player
- Windows Media Player (with appropriate plugins)
- Web browsers like Safari, Chrome, and Firefox (with HLS support)
5. Can I convert M3U8 to MP4?
Yes, you can convert M3U8 to MP4 using tools like FFmpeg. The process involves downloading the media segments listed in the M3U8 file and combining them into a single MP4 file.
6. How do I create an M3U8 file?
You can create an M3U8 file using a text editor by listing the media segments and their durations. Save the file with a .m3u8 extension and ensure it is encoded in UTF-8. For more details, refer to the steps outlined in the previous response.
7. What are the advantages of using M3U8?
- Adaptive Streaming: Adjusts video quality based on network conditions.
- Live Streaming: Suitable for live broadcasts.
- Resilience: Handles network interruptions better by requesting the next segment.
8. What are the disadvantages of using M3U8?
- Complexity: Requires a web server to host the media segments.
- Latency: May introduce slight delays in live streaming.
- Compatibility: Not all media players support M3U8 natively.
9. Is M3U8 suitable for offline playback?
No, M3U8 is designed for streaming and requires an internet connection to access the media segments. For offline playback, you should use formats like MP4.
10. How do I download videos from an M3U8 file?
You can use tools like FFmpeg or browser extensions to download and combine the media segments into a single video file. Refer to the previous response for detailed instructions.
11. Can I use M3U8 for audio streaming?
Yes, M3U8 can be used for audio streaming as well. The format is not limited to video and can list audio segments for streaming.
12. What is adaptive bitrate streaming?
Adaptive bitrate streaming is a technique where the quality of the video stream adjusts dynamically based on the viewer's internet connection speed. M3U8 files support this by listing multiple versions of the media at different bitrates.
13. What is HLS (HTTP Live Streaming)?
HLS is a streaming protocol developed by Apple that uses M3U8 files to deliver media content over the internet. It breaks the content into small segments and allows for adaptive bitrate streaming.

