Content Delivery Network Pricing Explained for Businesses
Content delivery networks (CDNs) have evolved from being a luxury to a necessity for businesses operating online. By distributing content across globally positioned servers, CDNs significantly reduce loading times, lower bandwidth costs at the origin, and enhance user experience regardless of where customers are located. For businesses competing in today's digital marketplace, these performance improvements directly affect conversion rates, search engine rankings, and ultimately, revenue.
Despite their critical importance, CDN pricing can be one of the most confusing aspects of web infrastructure for many business owners and IT managers. The industry employs various pricing structures, ranging from straightforward per-gigabyte rates to complex tiered models that include regional variations and feature-based premiums. This lack of clarity makes it difficult to budget accurately or compare providers on equal terms. As a result, many organizations either overpay for unused capacity or opt for inadequate solutions that compromise performance in an effort to reduce costs.
This guide aims to simplify CDN pricing and provide practical insights for making informed decisions. We will break down the advantages and disadvantages of each pricing model, examine the factors that influence your costs, and share strategies for optimizing your CDN investment without sacrificing performance. Whether you are looking for your first CDN solution or reevaluating your current provider, understanding these pricing fundamentals will help you balance performance needs with budget constraints.
Common CDN Pricing Models
CDN providers typically offer several pricing structures to accommodate different business needs:
Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) Model
The PAYG model charges based solely on actual usage, typically measured in gigabytes (GB) of data transferred. This model offers maximum flexibility with no upfront commitments.
Best for: Startups, small businesses, or websites with unpredictable traffic patterns.
Example: A small e-commerce site might pay only for the actual bandwidth consumed, which could range from minimal costs during quiet periods to higher amounts during sales or promotions.
Subscription-Based Model
This model involves fixed monthly or annual fees for a predetermined amount of data transfer or bandwidth. It provides more predictable costs for businesses with stable traffic patterns.
Best for: Medium-sized businesses with relatively consistent traffic.
Example: A news site with steady daily traffic might pay a fixed $200 monthly fee that covers up to 10TB of data transfer, providing cost certainty for budget planning.
Commitment-Based Model
In this model, businesses commit to a minimum spending level or data transfer amount over a contract period, often 12 months or more, in exchange for reduced rates.
Best for: Larger enterprises with predictable, high-volume traffic.
Example: A video streaming service might commit to transferring at least 100TB monthly for a year, receiving a 25% discount compared to standard rates.
Tiered Pricing Model
Tiered pricing offers different rates based on consumption levels, with costs per GB typically decreasing as usage increases.
Best for: Growing businesses expecting to scale their content delivery needs.
Example: A company might pay $0.085 per GB for the first 10TB, then $0.065 per GB for the next 40TB, and so on.
Hybrid Pricing Model
This approach combines elements of different models, such as a base subscription fee plus variable costs for usage beyond included amounts.
Best for: Businesses with a baseline of consistent traffic plus occasional spikes.
Example: A media company might pay a fixed fee covering 50TB of transfer monthly, with additional usage charged at competitive per-GB rates.
Factors That Influence CDN Pricing
Several variables can significantly impact the final cost of your CDN service:
Bandwidth and Data Transfer
The volume of data delivered to users remains the primary cost driver for most CDN services. Video content, high-resolution images, and large file downloads consume substantially more bandwidth than text-based content.
Geographic Coverage
Delivering content in North America and Western Europe typically costs less than serving users in other regions. CDN providers generally structure their pricing with these established markets as baseline rates, then apply variable premiums for global coverage. Asia-Pacific regions usually incur moderate surcharges, while content delivery to South America, Africa, and the Middle East often commands significantly higher rates due to limited infrastructure, higher operational costs, and fewer network interconnections.
Feature Sets and Security
Basic CDN services focus primarily on content delivery, while more comprehensive offerings include:
- SSL/TLS certificate management
- DDoS protection
- Web application firewalls (WAF)
- Bot management
- Advanced analytics
These enhanced features typically command premium pricing or require higher-tier service plans.
Additional Fees
Watch for these potential extra charges:
- HTTP/HTTPS request fees (charged per request rather than by volume)
- Cache invalidation/purging charges
- Origin shield costs
- Advanced routing features
- Premium support tiers
Pricing Examples from Major CDN Providers
To illustrate the range of pricing approaches, here's how some leading providers structure their costs:
Cloudflare
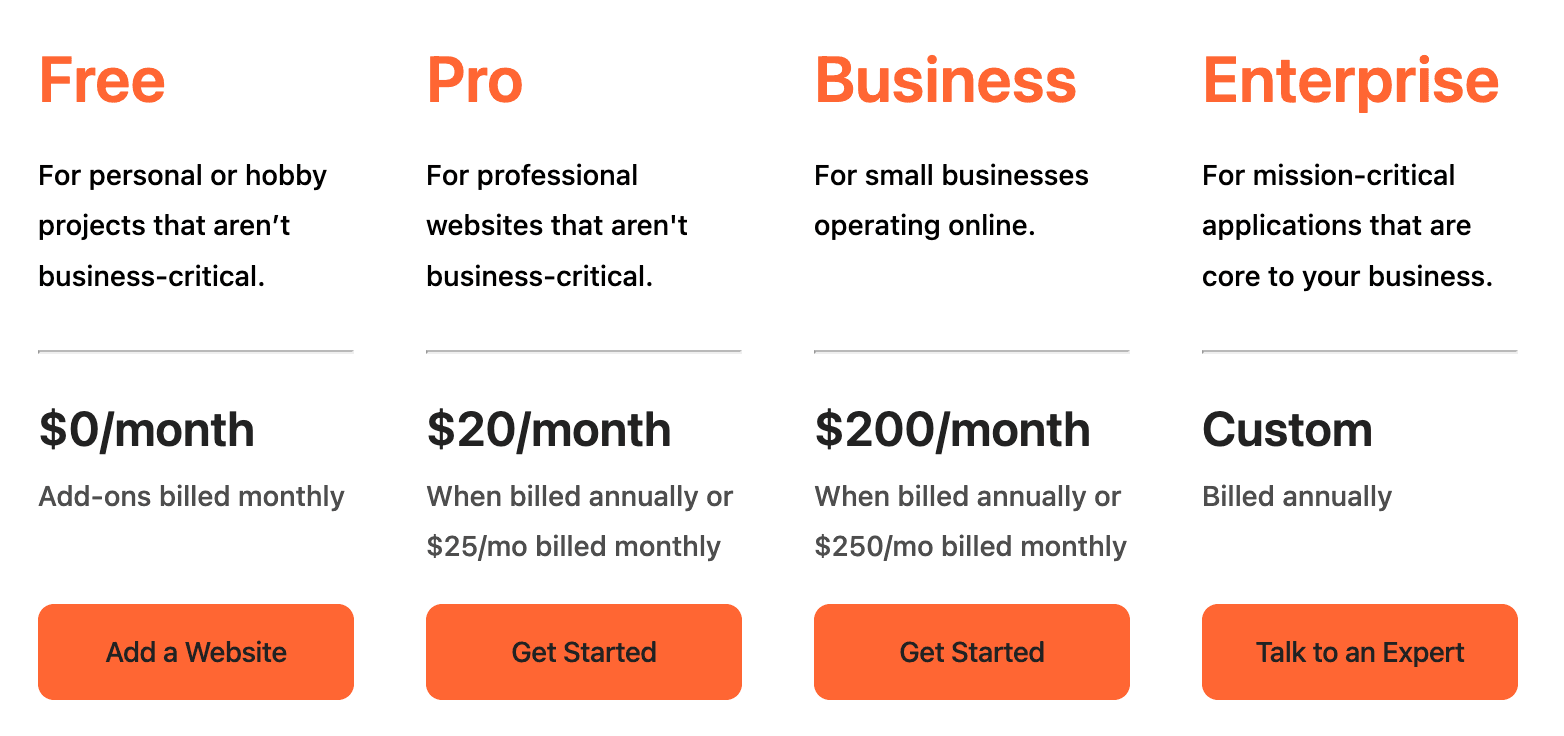
- Free Plan: Basic CDN functionality with limited features
- Pro Plan: $20/month with enhanced performance and additional features
- Business Plan: $200/month for advanced security and priority support
- Enterprise Plan: Custom pricing for organizations needing maximum performance, security, and support
Amazon CloudFront
Tiered pricing based on data transfer volume:
- First 1TB: Free
- Next 9TB: $0.085 per GB
- Next 40TB: $0.080 per GB
- Next 100TB: $0.060 per GB
- Next 350TB: $0.040 per GB
Google Cloud CDN
- Cache egress (data transfer): Starting at $0.08 per GiB
- Cache fill (origin fetch): $0.01-$0.04 per GiB
- HTTP/HTTPS cache lookups: $0.0075 per 10,000 requests
Finding Affordable CDN Solutions
If you're working with limited resources, you don't have to sacrifice quality. The market now offers several cost-effective CDN providers that deliver solid performance without the high prices. For a thorough comparison of affordable options, check out our detailed guide on the best affordable CDN services, where we evaluate providers that offer excellent value for small to mid-sized businesses.
Budget-friendly CDN solutions have significantly improved in recent years, with many now providing features that were once only available at enterprise price points. The key is to identify which features are most important for your specific needs, rather than paying for capabilities you won't use.
Strategies to Optimize CDN Costs
Implementing these approaches can help maximize the value of your CDN investment:
Understand Your Traffic Patterns
Analyze your traffic distribution by:
- Geographic regions
- Time of day/week
- Content types
- Seasonal variations
This data helps you select the most cost-effective pricing model and optimize content delivery settings.
Optimize Your Content
- Implement effective compression techniques
- Use modern image formats like WebP or AVIF
- Configure appropriate cache lifetimes
- Minimize unnecessary HTTP requests
Well-optimized content requires less bandwidth, directly reducing CDN costs.
Leverage Edge Computing
Many CDNs now offer edge computing capabilities that allow code execution closer to users. This can reduce origin traffic by:
- Transforming images at the edge
- Handling personalization without origin requests
- Implementing conditional origin calls
Select the Right Provider Mix
Consider using multiple CDN providers strategically:
- A low-cost provider for bulk static content
- A specialized provider for video streaming
- A security-focused CDN for sensitive transactions
Choosing the Right CDN for Your Business
When evaluating CDN pricing:
1. Start with your actual needs rather than comparing providers feature-by-feature
2. Request case-specific pricing based on your traffic patterns and content types
3. Factor in hidden costs like support, implementation, and integration expenses
4. Consider performance benefits that might offset higher direct costs through improved user experience and conversion rates
Conclusion
Content delivery network pricing doesn't need to be confusing. By understanding the various pricing models and factors that influence costs, you can make strategic decisions that balance performance requirements with budget constraints.
For most businesses, the ideal approach involves selecting a pricing structure that aligns with their typical usage patterns while providing flexibility for growth and traffic fluctuations. Remember that the cheapest option isn't always the most cost-effective when considering the full business impact of content delivery performance.
Looking for a CDN solution that delivers excellent performance without breaking your budget? EdgeOne offers a 14-day free trial with 1TB of included traffic, allowing you to test our global network before committing. With starter plans beginning at just $0.9 per month, we make enterprise-grade content delivery accessible to businesses of all sizes. Try EdgeOne today to see how we can optimize your content delivery while keeping costs predictable and affordable.