What is Function-as-a-Service?
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) is a form of cloud computing that empowers developers to execute applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. It provides an environment for designing microservices applications using event-driven computing. FaaS allows the execution of modular code snippets in response to specific triggers, thereby creating a "serverless" architecture. This approach simplifies operations, enabling developers to focus more on coding individual functions than managing servers or infrastructure, enhancing software delivery efficiency.
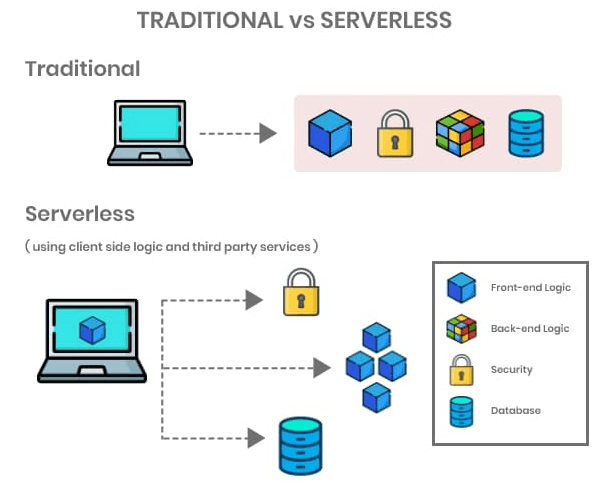
FaaS vs Serverless
FaaS (Function as a Service) and Serverless are two terms often used interchangeably in the context of cloud computing. However, they have distinct meanings and use cases. Here's a comparison of FaaS and Serverless:
Definition
- FaaS: Function as a Service is a specific type of serverless computing that allows developers to run individual functions or pieces of code in response to events without having to manage the underlying infrastructure. FaaS automatically scales, manages resources, and provisions the required infrastructure to execute the functions.
- Serverless: Serverless computing is a broader concept that encompasses FaaS but also includes other cloud computing services that abstract the underlying infrastructure management. In a serverless architecture, developers can build and deploy applications without worrying about the management of servers or other infrastructure components. The cloud provider handles the scaling, patching, and maintenance of the infrastructure.
Use Cases
- FaaS: FaaS is ideal for event-driven applications, such as real-time data processing, image or video processing, and IoT data processing. It is also suitable for microservices architectures, where individual functions can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
- Serverless: Serverless computing can be used in a wide range of applications, including web applications, APIs, data processing pipelines, and more. Serverless architectures can include FaaS, but they can also use other cloud services, such as databases, storage, and messaging systems.
In summary, FaaS is a specific type of serverless computing that focuses on running individual functions in response to events. Serverless is a broader concept that includes FaaS and other cloud services that abstract the infrastructure management. Both FaaS and Serverless aim to simplify application development and deployment by eliminating the need for developers to manage the underlying infrastructure.
How does FaaS Work?
Firstly, developers write snippets of code known as functions, which contain specific tasks or features. These functions are executed when a particular event occurs, such as an HTTP request, a database operation, or other user-defined events.
These functions are allocated to corresponding containers for execution in the computing resources. After execution, these containers are closed, and their computing resources are released. Therefore, users only pay for the computing resources used rather than for the resources needed to keep the server always open.
Thus, FaaS works "execution-on-demand"; functions are executed only when specific events are triggered. This allows developers to focus on writing business logic while ignoring the underlying runtime environment and hardware issues. Also, due to FaaS's high elasticity, it can quickly respond to workloads of various scales. So, what is the benefit of FaaS?
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of FaaS?
Advantages of FaaS
The benefits of Function as a Service (FaaS) can be summarized into several key points:
- Pay-as-you-go: FaaS effectively saves resources by charging only for what is actually used, avoiding the waste of idle resources.
- Automatic Scaling: FaaS can automatically respond to and adapt to changing business requirements without manual intervention, greatly optimizing resource allocation.
- Developer Focus: FaaS frees developers from tedious server and infrastructure management, allowing them to focus on code writing and optimization.
Through these benefits, Function as a Service (FaaS) optimizes the development process, reduces operating costs, and enhances productivity and system resilience. Having discussed the benefits of Function as a Service (FaaS), it's equally important to consider its potential drawbacks. While FaaS offers numerous advantages, such as resource savings, automatic scaling, and shifting the focus of developers, like any technology, it's not without flaws.
Disadvantages of FaaS
Function as a Service (FaaS) has a few potential drawbacks:
- Cold Starts: The delay when a function is invoked after idle can affect performance.
- Complexity: Implementing FaaS can be complex and requires a good understanding of the service to avoid issues.
- Debugging & Monitoring: Identifying and solving issues in a serverless architecture can be challenging.
- Vendor Dependency: Tying to a single provider may limit flexibility and lead to vendor lock-in.
The Relationship between IaaS, PaaS, and FaaS
In the world of cloud computing, Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) all play crucial roles. Their relationship can be understood through the lens of "levels of abstraction."
- IaaS: IaaS offers users a complete set of infrastructure resources, including virtual machines, storage, and network resources. Users have full control over these resources for application deployment and management. However, the burden of maintenance and configuration lies with the users themselves.
- PaaS: PaaS further abstracts the infrastructure, providing a direct application development and operation platform, including databases and middleware services. For developers, they only need to focus on the development of the application itself, without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- FaaS: FaaS is the highest level of abstraction. It requires developers to provide a piece of code executed when specific events are triggered. This further alleviates the burden on developers and enhances overall efficiency and performance. When no events need processing, these functions automatically shut down, thus conserving resources.
IaaS, PaaS, and FaaS offer varying levels of abstraction and control. Users can choose the service that best fits their needs and skills.
FaaS vs PaaS
In the field of cloud computing, Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) are both popular service models, but they have different features and applicable scenarios.
In FaaS, developers focus on individual functional code, with the platform automatically managing the underlying structure and triggering the code in response to specific events. FaaS can automatically shut down in the absence of event-driven, saving resources.
In contrast, PaaS provides a platform for developers to develop, run, and even scale applications without worrying about infrastructure. PaaS offers the development environment, runtime environment, operating system, etc., like Google App Engine. If an application needs to run continuously, requires more runtime environment and framework choices, and hopes to have better control over it, then PaaS may be a better choice.
In essence, the main difference between FaaS and PaaS is the level of abstraction they provide from the underlying infrastructure. FaaS provides a higher level of abstraction than PaaS, allowing developers to focus purely on their code and not worry about managing or scaling infrastructure. However, PaaS offers more environmental control, which can benefit more complex applications.
Why do Customers Choose Tencent EdgeOne Edge Function?
Tencent EdgeOne Edge Function is a serverless function computing service from Tencent Cloud designed to help users easily build edge computing applications. It allows users to run function code on edge nodes close to the user, thus realizing low latency, high availability, and scalability. Edge Function has the following features:
- Serverless Computing: Edge Function utilizes a serverless architecture, so users do not need to manage a server and can simply upload code to run on edge nodes.
- Low Latency: Edge Function is deployed on edge nodes worldwide, and users can choose the nearest edge node according to their geographic location to realize low latency access.
- Elastic Scaling: Edge Function automatically expands and shrinks function instances according to the call demand, improving resource utilization.
- Rapid Deployment: Users only need to write function code to deploy applications on Edge Function, shortening the uptime quickly.
Security and stability: Edge Function provides underlying computing resource management, including server CPU, memory, network, and so on, to ensure the safe and stable operation of services. - Integration with other services of Tencent Cloud: Edge Function connects with other cloud components through the event registration and callback mechanism and provides standard API interfaces, which makes it convenient for users to use other services of Tencent Cloud.
Feel free to contact us for more information.

