In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, delivering content quickly and reliably to a global audience has become a significant challenge. With the exponential growth of internet usage, businesses are under increasing pressure to provide seamless, high-performance access to their websites, applications, and streaming services. While traditional Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have played a crucial role in addressing these challenges through their distributed server networks, the growing complexity of the modern internet ecosystem has revealed the limitations of relying on a single-CDN architecture.
As user expectations continue to rise and digital infrastructure becomes more sophisticated, depending solely on one CDN provider can lead to considerable vulnerabilities, ranging from performance bottlenecks to system-wide outages. This is where Multi CDN solutions come into play as a transformative technology, offering organizations a more resilient, flexible, and efficient approach to content delivery.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of Multi CDN technology, discussing its fundamental concepts, operational mechanics, and the compelling reasons why it has become an essential component for businesses aiming to deliver exceptional user experiences in an increasingly connected world.
What is a CDN?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a sophisticated infrastructure consisting of globally distributed servers that deliver web content and media to users based on their geographic location. By intelligently caching content at strategic locations worldwide, CDNs significantly reduce latency and improve loading speeds. This advanced network acts as an intermediary between the origin server (where the content is hosted) and the end-users, ensuring optimal content delivery through the nearest available server. This revolutionizes the traditional process of content delivery.
The CDN architecture includes three key components: edge servers, origin servers, and Points of Presence (PoPs). Edge servers serve as local content caches, strategically positioned to efficiently handle user requests, while origin servers maintain the authoritative source of the content. PoPs are strategically located data centers that house edge servers and networking equipment, forming the backbone of the CDN infrastructure. This distributed network ensures that content is cached and delivered from optimal locations, minimizing response times and reducing the load on origin servers by effectively distributing traffic.
CDNs offer multiple essential advantages for modern businesses, including significantly improved content delivery speeds, optimized bandwidth costs, enhanced website performance, and strong security protections. By reducing the physical distance that data must travel, CDNs ensure faster loading times and a better user experience across all regions. Additionally, they lower infrastructure costs by distributing traffic across edge servers, preventing server overload and potential downtime. Importantly, CDNs also provide advanced security features, such as sophisticated DDoS protection and threat mitigation capabilities, ensuring that websites remain secure and accessible even under challenging conditions.
What is Multi CDN?
Multi CDN is an advanced content delivery strategy that utilizes multiple CDN providers simultaneously to create a more robust and efficient distribution network. This approach leverages each provider's unique strengths, geographical presence, and performance characteristics to optimize content delivery on a global scale. By intelligently using multiple CDN infrastructures, organizations can achieve superior content delivery performance, enhanced reliability, and extensive geographical coverage, while ensuring seamless failover capabilities in the event of regional outages or performance degradation.
Unlike traditional single-CDN architectures, Multi CDN implementations dynamically distribute traffic across various providers. This significantly reduces the risks associated with provider-specific failures or performance bottlenecks. The intelligent traffic distribution system continuously evaluates real-time performance metrics, network conditions, and geographical factors to determine the optimal CDN for each user request. As a result, organizations benefit from a more resilient content delivery infrastructure that maintains consistent performance levels and ensures uninterrupted service availability, even during challenging network conditions or provider-specific issues.
At the core of a Multi CDN architecture are several sophisticated components working together: an intelligent load balancer for traffic distribution, an advanced traffic management system for real-time optimization, and comprehensive monitoring tools for performance analysis. These systems collaboratively analyze various parameters, including latency, throughput, error rates, and geographical proximity, allowing for split-second decisions to route each request through the most efficient path. This dynamic orchestration ensures optimal content delivery performance while maintaining system reliability through automated failover mechanisms and continuous performance optimization.
How Multi CDN Works?
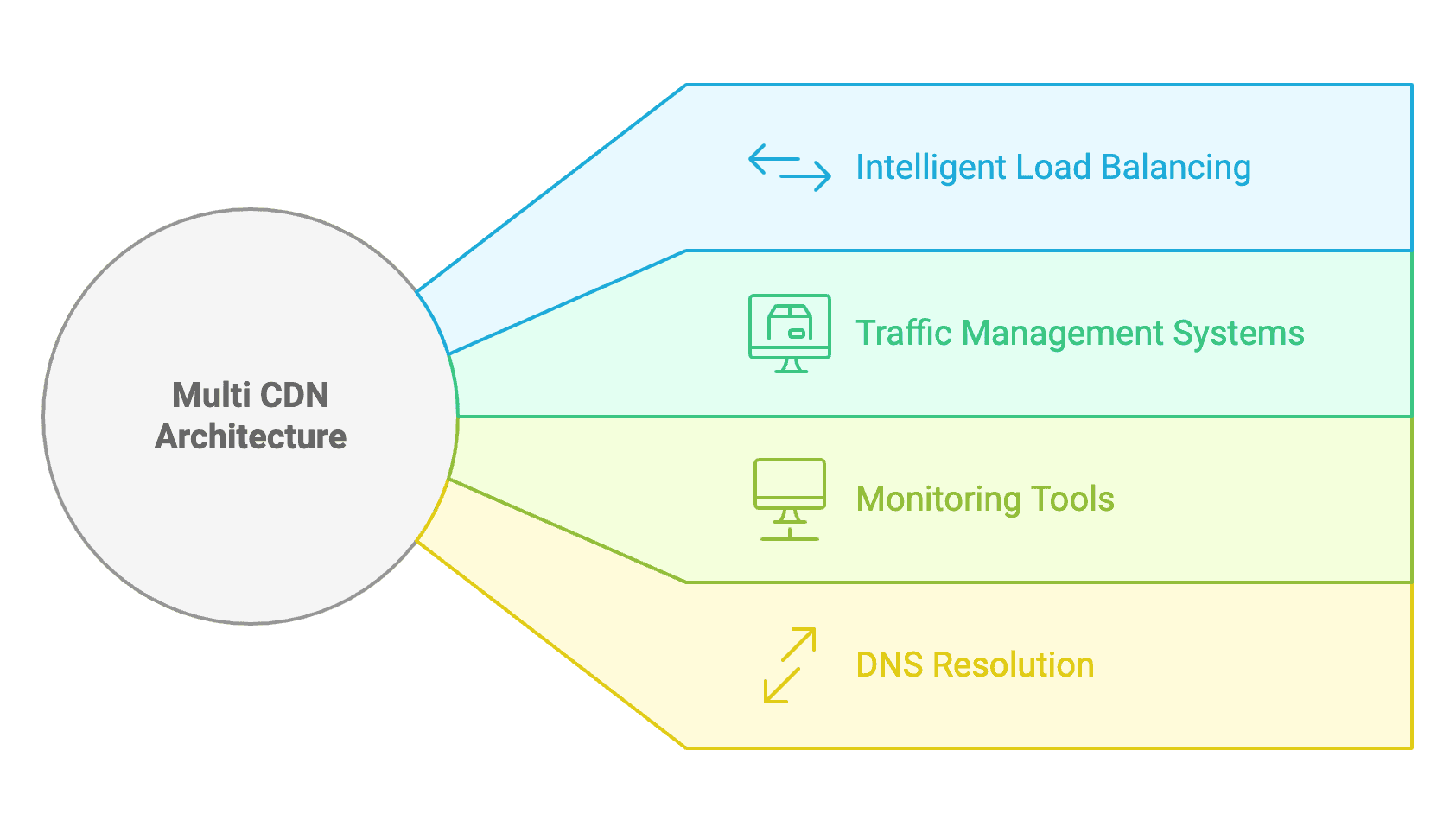
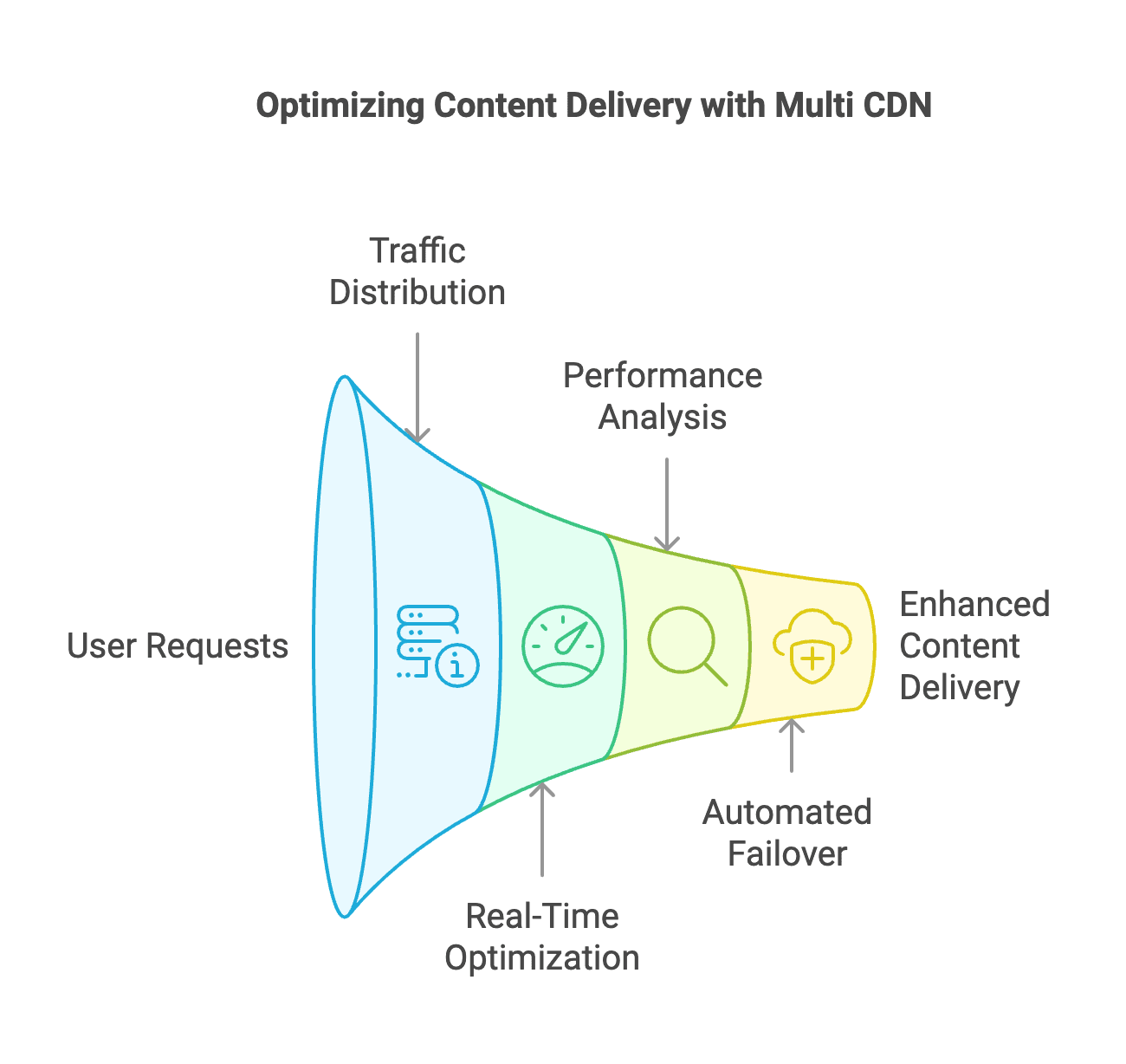
A Multi CDN architecture integrates several CDN providers into a unified system, allowing for dynamic traffic routing based on real-time performance metrics. This advanced infrastructure combines load balancers, traffic management systems, and monitoring tools to optimize content delivery across different providers. The system continuously evaluates performance metrics to ensure the best routing decisions.
The core operation of a Multi CDN relies on intelligent load balancing, which distributes user requests among various CDN providers. Using advanced algorithms, the load balancer takes into account factors such as server availability, network latency, and geographic location to determine the optimal CDN for each request. This approach ensures efficient resource utilization and helps prevent performance bottlenecks across the network.
Traffic routing in Multi CDN deployments uses dynamic algorithms that adjust to changing network conditions. The system monitors real-time performance metrics from each CDN provider, including response times, error rates, and bandwidth utilization. Based on this data, the traffic management system automatically modifies routing rules to maintain optimal delivery paths and ensure consistent performance.
The DNS resolution process plays a crucial role in Multi CDN operations by directing users to the most suitable CDN provider. When users request content, the DNS resolver works with the traffic management system to identify the best provider based on current conditions. This decision-making process considers factors such as server load, network status, and geographic proximity, ensuring fast and reliable content delivery to end users.
Key Benefits of Multi CDN
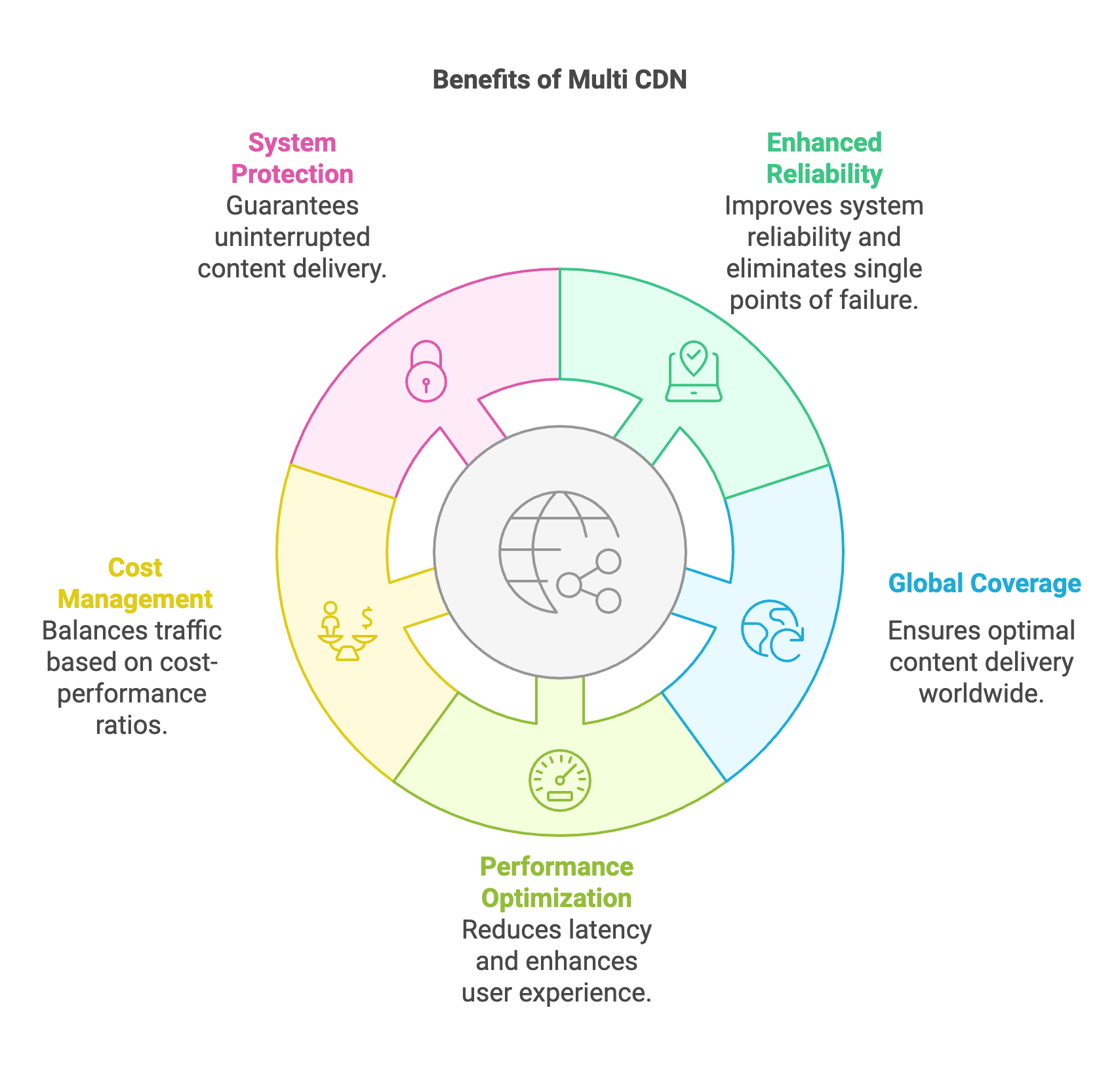
1. Enhanced Reliability and Redundancy
Multi CDN solutions greatly improve system reliability and redundancy by distributing content delivery across multiple providers. This setup eliminates single points of failure, as traffic can be quickly redirected when one CDN encounters issues. The redundant infrastructure ensures continuous service availability and maintains consistent performance levels, making it especially valuable for business-critical applications and high-traffic websites.
2. Comprehensive Global Coverage
Global coverage is significantly enhanced through the strategic use of multiple CDN providers, each excelling in specific geographic areas. By combining their strengths, businesses can create a worldwide network that ensures optimal content delivery to users, regardless of their location. This approach results in consistent performance across diverse international markets.
3. Dynamic Performance Optimization
Performance optimization is achieved through intelligent traffic routing and real-time monitoring of the CDN network. The system continuously analyzes metrics such as response times, server load, and network conditions to route requests to the most efficient provider. This dynamic routing mechanism reduces latency, speeds up content delivery, and enhances the user experience across all regions.
4. Strategic Cost Management
Cost efficiency is attained through sophisticated traffic distribution algorithms that consider both performance and pricing factors. By leveraging the varying cost structures and regional pricing models of different providers, organizations can optimize their content delivery expenses. The system automatically balances traffic based on cost-performance ratios, ensuring optimal resource utilization while maintaining service quality.
5. Robust System Protection
System resilience is significantly improved through the implementation of automatic failover mechanisms and redundant delivery paths. When service disruptions occur with one provider, the system seamlessly redirects traffic to alternative CDNs, ensuring uninterrupted content delivery. This robust architecture provides essential protection against outages and guarantees consistent service availability, making it invaluable for organizations that require high reliability.
Single CDN vs Multi CDN
Below is a comprehensive comparison between Single CDN and Multi CDN architectures:
| Aspect | Single CDN | Multi CDN |
| Architecture | Uses one CDN provider | Utilizes multiple CDN providers simultaneously |
| Performance |
|
|
| Reliability |
|
|
| Coverage |
|
|
| Cost |
|
|
| Implementation |
|
|
| Management |
|
|
| Security |
|
|
| Load Balancing |
|
|
| Analytics |
|
|
| Best For |
|
|
When choosing between Single CDN and Multi CDN solutions, organizations should consider these key factors:
- Cost and Performance: Single CDN is cost-effective for predictable, moderate traffic. Multi CDN excels in high-volume, global traffic scenarios.
- Operational Complexity: Single CDN is easier to manage with lower overhead. Multi CDN requires more expertise and resources.
- Service Level Agreements (SLA): Managing SLAs is simpler with a Single CDN. Multi CDN offers more extensive guarantees.
- Scalability: Single CDN may have limitations based on the provider. Multi CDN provides flexible growth across various providers.
Organizations should assess these factors against their specific needs and resources to make an informed choice for their content delivery strategy.
Common Use Cases for Multi CDN
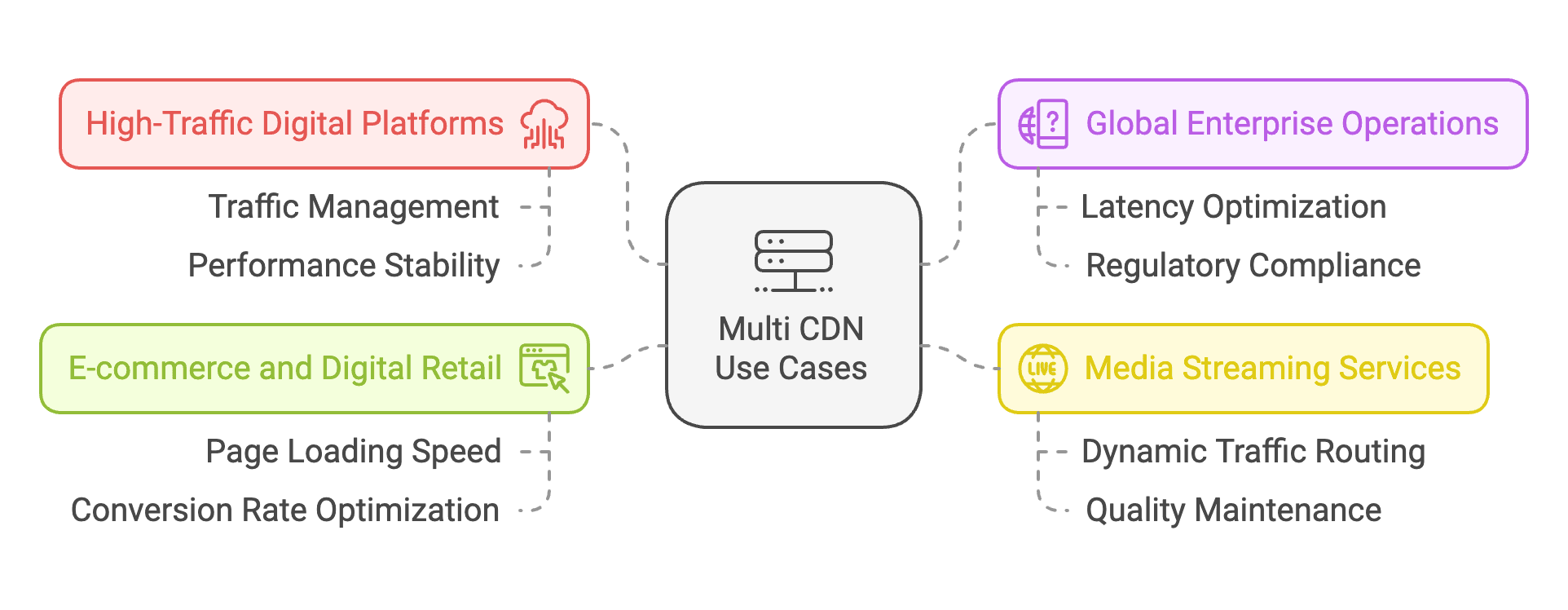
1. High-Traffic Digital Platforms
Large-scale websites and digital platforms use Multi CDN solutions to manage significant traffic volumes and ensure consistent performance. These platforms often experience unpredictable traffic spikes and require a robust infrastructure to maintain stability. By distributing requests across multiple CDN providers, the system prevents server overload, ensures optimal response times, and maintains high availability during peak periods, making it essential for mission-critical online operations.
2. Global Enterprise Operations
International businesses with a diverse geographical presence implement Multi CDN strategies to deliver consistent user experiences worldwide. This approach enables content delivery from strategically positioned edge locations, minimizing latency and optimizing performance across different regions. The system intelligently routes traffic based on user location and network conditions, ensuring efficient content delivery while maintaining compliance with regional data regulations and performance requirements.
3. Media Streaming Services
Streaming platforms rely on Multi CDN architecture to deliver uninterrupted, high-quality video content to their global audience. The system dynamically routes streaming traffic through the most efficient paths, considering factors such as bandwidth availability, network congestion, and server load. This sophisticated approach ensures smooth playback, minimizes buffering, and maintains consistent video quality, which is crucial for user retention and satisfaction in the competitive streaming market.
4. E-commerce and Digital Retail
Online retail platforms utilize Multi CDN solutions to create seamless shopping experiences and optimize conversion rates. The system ensures rapid page loading times, swift image delivery, and responsive user interfaces across all devices and locations. By leveraging multiple CDN providers, e-commerce platforms can maintain high performance during sales events, reduce cart abandonment rates, and provide reliable service during peak shopping periods, ultimately impacting revenue and customer satisfaction.
Choosing Multi CDN Providers
1. Important Factors to Consider
When selecting Multi CDN providers, it is essential to consider several factors: performance, coverage, cost, support, and integration capabilities. Performance is a critical factor as it directly affects the user experience. Evaluate the performance of each CDN provider across different regions and under various conditions to ensure they meet your requirements. Coverage is also crucial; it indicates the geographic reach of the CDN. Choose providers that have extensive coverage in the regions where your users are located. Cost is another significant consideration, as pricing models and structures can vary by provider. Assess the cost-effectiveness of each option and see how they align with your overall budget. Additionally, consider support and integration capabilities, as these determine how easily you can incorporate and manage the CDN providers within your Multi CDN setup.
2. Popular Multi CDN Providers
Some well-known Multi CDN providers include Akamai, Cloudflare, Fastly, Amazon CloudFront, and EdgeOne. Each of these providers has unique strengths, making them suitable for different use cases and requirements. Akamai is recognized for its extensive global network and high performance, making it a popular choice for large-scale websites and streaming services. Cloudflare offers a variety of security features and performance optimizations, making it ideal for businesses seeking to enhance both performance and security. Fastly stands out for its real-time content delivery and edge computing capabilities, making it suitable for dynamic content and applications. Amazon CloudFront provides seamless integration with other AWS services, which is beneficial for businesses already using the AWS ecosystem. EdgeOne offers comprehensive performance and security features, making it a versatile choice for various use cases.
3. Comparison Criteria
When comparing providers, consider criteria such as network reach, performance metrics, pricing models, and customer support. Network reach indicates the geographic coverage of the CDN, so opt for providers that offer expansive coverage in the regions where your users are located. Performance metrics, such as latency, throughput, and error rates, provide insights into the performance of each provider. Evaluate these metrics to ensure the providers meet your performance requirements. Pricing models and structures differ among providers, so assess the cost-effectiveness of each option and how they fit into your overall budget. Customer support is also vital as it impacts how easily you can obtain assistance and resolve any issues that may arise.
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
1. Essential Performance Metrics
To effectively monitor Multi CDN performance, it's crucial to track key metrics that influence content delivery. Important indicators include latency measurements, which quantify the speed of data transmission between servers and end-users; throughput rates, which assess data transfer capacity; and error frequencies, which indicate the reliability of the system. Advanced user experience metrics provide deeper insights into content delivery quality by incorporating factors such as Time to First Byte (TTFB), page load times, and user engagement metrics. Together, these measurements offer a comprehensive view of system performance and help identify areas for optimization.
2. Advanced Monitoring Solutions
Modern monitoring platforms offer sophisticated tools for real-time tracking and analysis of multiple CDN providers. These systems feature comprehensive dashboards that display real-time metrics, analyze historical trends, and provide predictive analytics capabilities. Leading solutions like Cedexis, Catchpoint, and Datadog come equipped with advanced features, including automated alerting systems, detailed performance reports, and customizable monitoring parameters. Such tools enable organizations to maintain proactive oversight of their content delivery infrastructure and respond rapidly to performance variations or potential issues.
3. Strategic Optimization Techniques
Optimizing a Multi CDN requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technical enhancements with strategic planning. This includes continuously adjusting load balancing algorithms to ensure optimal traffic distribution, regularly updating routing rules based on performance data, and implementing sophisticated caching strategies. Advanced compression techniques and content optimization methods further enhance delivery efficiency. Organizations should also conduct regular performance testing to validate their optimization efforts and discover new opportunities for improvement, ensuring the system operates at peak efficiency under varying conditions.
4. Data-Driven Performance Testing
A/B testing is a critical tool for validating and refining Multi CDN configurations. This method involves creating controlled experiments to compare different routing strategies, caching configurations, and optimization techniques. By systematically analyzing the performance data from these tests, organizations can make informed decisions about system improvements. This iterative testing process allows for continuous optimization of the content delivery infrastructure, resulting in enhanced performance metrics and improved user experiences across all service regions.
Conclusion
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, Multi CDN technology is crucial for organizations aiming to optimize their global content delivery systems. This advanced approach not only improves performance and reliability but also offers strategic advantages in a competitive digital marketplace. By utilizing multiple CDN providers, organizations can achieve exceptional service availability, optimize costs through smart traffic distribution, and provide excellent user experiences across various geographic regions.
Successfully implementing Multi CDN requires a comprehensive strategy, including careful selection of providers, robust integration practices, and ongoing performance optimization. Organizations must monitor performance closely and use data-driven techniques to ensure maximum system efficiency. As digital transformation accelerates, the importance of Multi CDN in enabling seamless, secure, and high-performance content delivery becomes even more vital.
Ready to optimize your content delivery strategy? Discover how EdgeOne can help you seamlessly navigate the choice between Single CDN and Multi CDN solutions. Sign up now for a free trial and experience firsthand how our innovative platform can enhance your performance, scalability, and operational efficiency. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and take the first step towards a more effective content delivery solution with EdgeOne!

