Mobile Integration Overview
Overview
Client attestation ensures each API request carries a valid attestation token, thereby verifying the request originates from a trusted mobile app and effectively resists malicious requests. Unlike the automatic interception mechanism for web or WebView clients, mobile client integration requires developers to adapt at the application layer to achieve request sending, attestation token retrieval and attachment, and server challenge response.
Compatibility
EdgeOne Client Attestation SDK supports the following mobile terminals:
iOS 11 or higher operating system.
Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher operating system.
Mobile SDK Operation Mechanism Overview
The EdgeOne Client Attestation SDK operates in iOS or Android environments, with its core mechanism built around collaboration between client applications, the SDK, attestation service, and EdgeOne. Developers proactively call the SDK API in application code to implement a complete attestation process.
Note:
Developers need to explicitly handle HTTP 428 responses in code, call the SDK for attestation challenge, then add the obtained token to subsequent requests. The SDK is responsible for attestation logic execution and token generation and management, but request sending, response capture, and retry logic must be implemented at the application layer.
Here is how it works:
1. API request initiation: The mobile application initiates an API request to the backend service protected by EdgeOne. The initial request may not include an attestation token or may contain an expired/invalid token.
2. EdgeOne attestation challenge: After receiving the request, EdgeOne performs validation based on the configured attestation policy. If the request does not meet attestation requirements (such as lack of token or invalid token), EdgeOne will return HTTP 428 status code and carry an attestation challenge ID in the response header
EO-Attest-Challenge.3. Client handles the challenge: After receiving the HTTP 428 response, the mobile application needs to extract the
EO-Attest-Challenge ID from the response header. Subsequently, the app calls the SDK's attestWithParams() API and imports this challenge ID. The SDK will execute the appropriate attestation process based on the challenge type (such as Captcha or invisible verification). For detailed client attestation process, refer to the product description (see: Tencent Cloud Captcha, Tencent Cloud Risk Control Engine).4. SDK interacts with the attestation service: After receiving the challenge ID, the SDK interacts with the EdgeOne attestation service to complete the client attestation process. This may involve displaying a verification code interface in
WKWebView for user interaction or executing proof-of-work in the background.5. Obtain attestation token: After attestation succeeded, the SDK will generate a valid attestation token. The app obtains this token via the interface provided by the SDK (such as
getAttestationToken()).6. Resend request: The app adds the newly obtained attestation token to the
EO-Attest-Token HTTP header of the original API request and resends it.7. EdgeOne proceeds with the request: After receiving the request with a valid attestation token, EdgeOne verifies the token's validity and allows the request to flow to the backend service.
Attestation Credential Token Workflow
The attestation token is a key credential that establishes trust between the client and EdgeOne attestation service. In iOS or Android applications, developers need to understand and correctly handle the attestation token lifecycle, including obtaining, using, and renewing.
Obtaining a New Attestation Credential Token (Or Manual Attestation)
In some scenarios, you may need to actively trigger client attestation to retrieve a new attestation token, for example:
Before the first request: After the application launches, you can actively call the SDK for attestation before sending the first request to the protected API to avoid receiving a 428 challenge on the first request.
Handling HTTP 428 Challenge: When receiving an HTTP 428 status code returned by the server, extract the challenge ID and call the SDK API to initiate the attestation challenge.
Mandatory attestation: When the business logic requires forcing user attestation.
You can initiate the attestation challenge by calling the SDK's
attestWithParams() method. This method executes the attestation process based on the challenge parameters and returns the attestation token via AttestCallbackDelegate upon success.Note:
After each successful call to
attestWithParams(), the SDK generates or updates the attestation token. Before attaching the token to request headers, be sure to call getAttestationToken() again to get the latest token. Each time you need to use token data, please retrieve new token data. Do not save or reuse the token data returned by getAttestationToken().Using Existing Attestation Token
Once the attestation token is successfully acquired, the SDK will cache it internally. Within the token's TTL, you can reuse this cached token without the need to re-execute the attestation challenge each time. Even if the app is suspended in the backend or wakes up from idle status, the SDK provides a valid cached token.
When sending a request to a protected API, you need to get the current valid attestation Token from the SDK and add it to the
EO-Attest-Token header of the HTTP request. The SDK provides the getAttestationToken() method to obtain this Token.Reobtaining an Attestation Token or Renewing an Expired Attestation Token (Handling HTTP 428 Challenge)
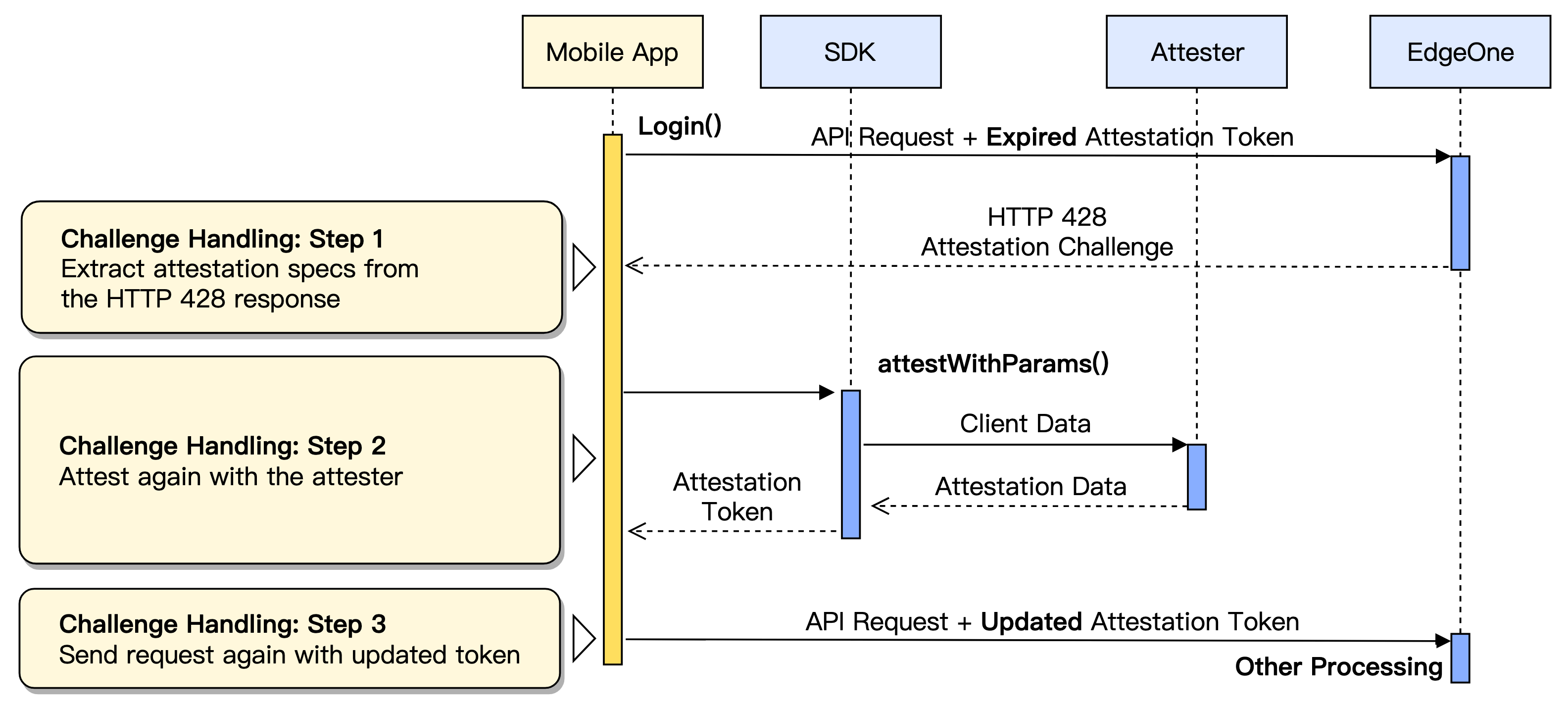
The attestation token has a valid period. When the token expires or becomes invalid for other reasons, the EdgeOne server will return an HTTP 428 status code to indicate the client needs to authenticate again. This is one of the most important adaptation steps in iOS and Android client integration.
Your application needs to implement a healthy mechanism to capture and address HTTP 428 responses. A typical workflow is as follows:
1. Capture 428 response: In your network request callback, check the HTTP response status code. If it is 428, it indicates an attestation challenge is needed.
2. Extract challenge ID: Extract the attestation challenge ID from the
EO-Attest-Challenge response header in the HTTP 428 response. This is the credential to initiate a new attestation challenge.3. Execute attestation challenge: Call the
attestWithParams() method of the SDK and input the extracted challengeId. If the authenticator requires user interaction (such as Captcha), you also need to provide a WKWebView instance.4. Obtain new token: After the attestation challenge succeeds, get the latest attestation token generated by the SDK via
getAttestationToken().5. Resend request: Add the new token to the
EO-Attest-Token header of the original API request and resend it. At this point, the request should pass EdgeOne's attestation and flow normally to the backend service.Using WKWebView or WebView for Interactive Attestation (And JS Attestation)
In some client attestation scenarios, the authenticator may require user interaction (e.g., interactive Captcha) or execute compute-intensive tasks (e.g., Proof of Work encryption). At this point, the EdgeOne SDK needs specific environment support. On mobile platforms,
WKWebView (iOS platform) or WebView (Android platform) are key components to implement these features.Note:
In the following content,
WebView will be used to unify the reference to corresponding components on different platforms, namely: WKWebView (iOS platform) or WebView (Android platform). Use the actual platform component name for adaptation.When the authenticator needs to render an interactive CAPTCHA or run a JavaScript-based Proof-of-Work encryption challenge, the SDK requires a
WebView instance to be provided when calling the attestWithParams() method. This means developers must allocate a WebView instance in advance in the application and pass it as an argument to the SDK when calling the attestation API.Interactive Attestation Scenario
Some authenticators (such as TC-CAPTCHA using embedded or pop-up interaction settings) require a
WebView instance to render their interactive interface. This WebView instance will display the verification code webpage within the application, so it must be preset to ensure correct display.Embedded Interactive Attestation: The CAPTCHA interface is displayed in a fixed block form on the device screen. To ensure the UI displays correctly without affecting user experience, developers must preset the rendering window's size, layering sequence, and alignment mode. Please note, the embedded attestation GUI does not scale with the screen view. For example, TC-CAPTCHA embedded mode recommends reserving at least 300x230 pixel space to get the best rendering effect and user interaction experience.
Pop-up Interactive Attestation: The CAPTCHA interface appears as a floating window on the device screen when attestation is triggered. Similar to embedded attestation, the rendering window's size, layering sequence, and alignment mode must also be preset. The pop-up attestation feature is that when the screen view is less than a specific threshold, the pop-up attestation GUI automatically scales to adapt to different screen sizes. For example, the initial rendering block size for TC-CAPTCHA pop-up mode is 360x360 pixels.
JavaScript-Based Attestation Scenario
Some authenticators (such as TC-CAPTCHA in seamless mode) require a
WebView instance as the JavaScript runtime environment, primarily used to execute encrypted Proof of Work (PoW) challenges. In this scenario, the WebView instance provides only a JavaScript execution sandbox, with no need to visibly render any UI. Therefore, the passed-in WebView instance does not need to be visible, and the SDK will not use it for UI rendering.Validating Integration
To ensure stable operation of the EdgeOne client attestation SDK in your application, refer to the following KPIs to determine whether integration is successful (recommend troubleshooting sequentially):
Verification Item 1: Client Access to EdgeOne Edge Service
Client attestation requires your client to access the EdgeOne service. If your business uses multiple CDN service providers, only the portion served by EdgeOne supports client attestation.
Ensure the response you received includes the
EO-LOG-UUID header. If the header is not included in the response, the client may have accessed a service other than EdgeOne.
Verification Item 2: SDK Successfully Loaded
The SDK must be successfully loaded to complete the required client attestation process.
After the SDK is successfully loaded, it will access the /.eo-sec-bot/ service in the business domain for initialization. If this request is not observed, the SDK may have an initialization exception.
Verification Item 3: Complete Client Attestation Rule Configuration
Client attestation rules define the specific attestation requirements of business services for clients. You need to complete configuring client attestation rules before performing the automated attestation process.
After the client attestation rules are configured correctly, when a client attempts to directly access a protected API without carrying out any attestation process, it will receive an HTTP 428 challenge response. This response will carry the
EO-Attest-Challenge header.Note:
When no client attestation rule is configured, you can still manually initiate the attestation process by calling the
attestWithParams() API on the client. However, since the server API is unprotected, EdgeOne will not validate attestation credentials or respond to the HTTP 428 challenge.If the client does not receive an HTTP 428 challenge, refer to the following process to troubleshoot:
1. Check whether the client's API request accesses the correct domain name
Check whether the domain accessed by client has been parsed to EdgeOne's access via CNAME and can normally access EdgeOne edge nodes.
2. Check whether the client request is blocked by another security policy
If the client receives an interception status code such as HTTP 567, record the EO-LOG-UUID header content in the response and use the request ID as a filter condition in Web security analysis to confirm the specific interception reason.
3. Check whether the client's API request correctly matches the client attestation rule
First, confirm the Web protection policy used for the domain name (site-level policy, domain-level policy, or policy template). On the site's Web protection configuration page, select the corresponding policy and perform further configuration check.
Then, confirm whether the rule is configured and enabled in Bot Management > Client Attestation. The match condition of the rule should include the request scope, and the policy settings should cover the corresponding client type.
Verification Item 4: Client Correctly Handles HTTP 428 Challenge
The client must correctly handle the challenge response to perform adaptive attestation, renewal, and other processes.
When the client receives the
HTTP 428 challenge response, it will perform the attestation process, then initiate the request again.Note:
If your client attestation rule configuration uses multiple attestation methods for an API resource (for example: multiple rules are configured to protect an API resource, or SDK challenge is used for secondary attestation), your client will receive multiple HTTP 428 requests. Ensure your client re-initiates the request after processing each challenge.
Verification Item 5: Rendering of Interactive Attestation (Selectable)
If your application uses interactive attestation (for example: interactive Captcha), please ensure its UI can render correctly and respond to user actions.
Trigger the attestation process and verify the rendering position of interactive attestation. After completing attestation, confirm the operation process completes normally.