Cache Prefresh
Feature Introduction
After the cache resources expire within the EdgeOne node, EdgeOne will follow the origin to obtain the latest resource files when receiving the corresponding client requests, which may cause a large increase in origin-pull requests during peak periods. The cache pre-refresh function can verify the validity of cache resources before they expire, without waiting for expiration, which helps maintain the real-time nature of resources and respond to requests more quickly. The cache pre-refresh time can be configured according to the percentage of the file cache TTL.
Usage Scenarios
Since the cache pre-refresh function can verify the validity of resources in advance, it is suggested to use it in scenarios where content needs to be frequently updated or user experience is highly demanded:
High Real-time Requirements: For content that needs to be updated quickly, such as news, event pages, etc., customers hope that users can obtain the latest resources when requesting. By enabling the cache pre-refresh function, the node verifies and updates the cache before the resources expire, ensuring that users can obtain relatively new resources when accessing, thus avoiding additional waiting time when users request and improving user experience.
Reduce Origin-pull Pressure: For some hotspot resources, a large number of origin-pull requests may be triggered after expiration. Enabling the cache pre-refresh function can advance these origin-pull requests, reducing the concentration of a large number of origin-pull requests when resources expire, thereby reducing origin-pull pressure.
Directions
Scenario One: Configure cache pre-refresh for all domain names of the site
If you need to configure the same cache pre-refresh for the whole connected site, or as a site-level fallback configuration, please refer to the following steps:
1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the Site Global Configuration page. In the right-hand navigation bar, click Cache Configuration.
3. Locate the Cache Pre-refresh card, click Switch, and enter the percentage value for the pre-refresh time in the pop-up confirmation box.
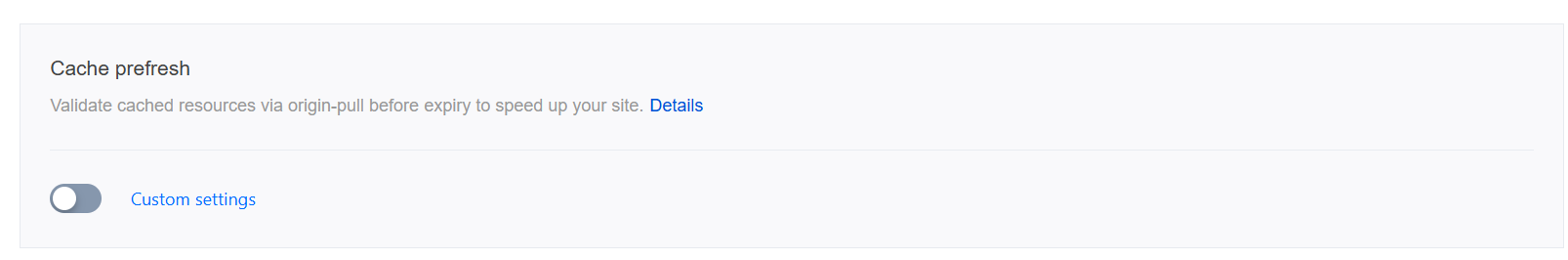
Configuration state: Default is enabled, can be turned off by clicking the slider.
Pre-refresh Time: The percentage of the node cache TTL, can enter an integer between 1-99. Default is 90%.
Scenario Two: Configure cache pre-refresh for specific domain names, paths, or file extensions, etc.
If you need to configure different cache pre-refresh for different domain names, paths, or file extensions, etc., for example: Configure a more advanced pre-refresh time - 60% for the
www.example.com domain under the example.com site. Please refer to the following steps:1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global site configuration page, then click the Rule Engine tab.
3. On the rule engine management page, click Create rule and select Add blank rule.
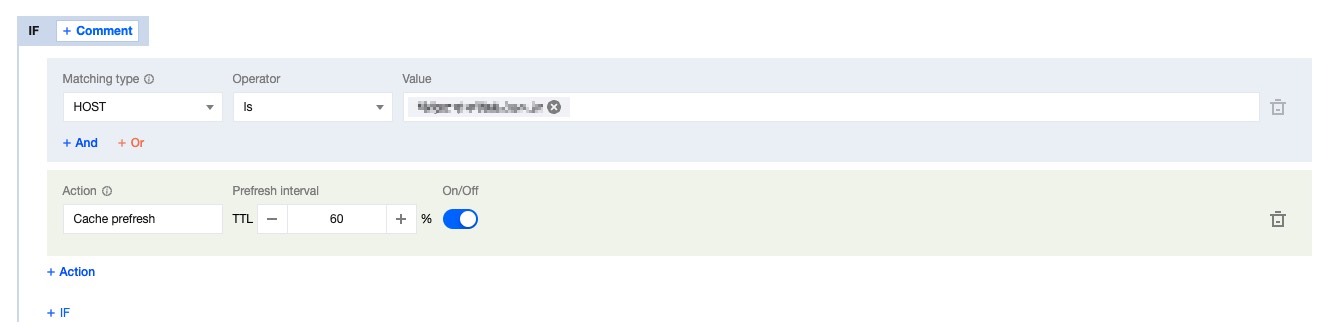
4. On the rule editing page, select Host as the matching type and configure it as
www.example.com.5. Click on the Action, and in the pop-up operation list, select the operation as cache pre-refresh, and configure it as 60% of the TTL.
6. The complete configuration is shown below, click Save and Publish to complete the rule configuration.
Attachment: Functional Principle
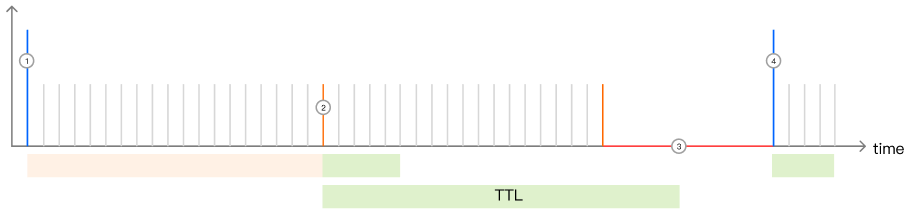
Assuming that the specified image
test.jpg has a node cache TTL of 10 seconds and a cache pre-refresh time of 80% of the TTL (i.e., 8 seconds), then:1. When the node receives the client request for the first time, the current node does not cache the file, and it will follow the origin to pull the resource and cache it in the node, with a cache TTL of 10 seconds. Within 0-7 seconds, if the client request is received again, the node will directly provide the resource from the cache and normally respond to the client request;
2. When the
test.jpg cached in the node reaches the pre-refresh time, between the 8th and 10th seconds, if the client request is received, the node will still normally respond to the client request, but at the same time, it will asynchronously follow the origin to verify whether the cache resource is valid;If the resource is valid, the cache TTL of the resource on the node will be updated and reset to 10 seconds;
If the resource is invalid, the latest valid resource will be obtained from the origin to the node, and the node cache TTL will be reset to 10 seconds;
3. If no client requests are received after the file exceeds the node cache TTL, the cache will exceed the cache.
4. When the node receives a Client request next time, the node will send an origin-pull request to the origin to verify whether the resources are valid. If the file is updated, the latest file will be pulled, otherwise, the file will be cached again and the Cache time will be refreshed to 10 seconds.