Range GETs
Overview
Range GETs can be enabled to reduce the consumption of large file origin-pulls and response time.
Why can Range GETs improve the efficiency of large file delivery?
When caching large files, nodes will split them into smaller parts in order to improve cache efficiency. All parts cached expire at the same time and follow the node cache TTL configuration. Range requests are also supported. For example, if a client request carries the HTTP header
Range: bytes = 0-999, only the first 1000 bytes of the file will be returned to the user.If Range GETs is enabled: When parts of the file are requested and their caches expire, nodes only pull and cache the requested parts and return them to the user, so that origin-pull consumption and response time are greatly reduced.
If Range GETs is disabled, when the client requests only parts of a file, the node will pull only the requested parts according to the
Range header in the client request, cache them, and return them to the client at the same time. However, this may not be able to achieve the optimal performance. In large file scenarios, we recommend you enable Range GETs.Use Cases
You can use Range GETs to cache large static files in either of the following cases: The origin server supports Range requests, or you use a Tencent Cloud COS origin server and do not apply any data processing methods such as image processing.
Notes
The origin server must support Range requests, or the origin-pull may fail.
The origin-pull may fail if Range GETs is enabled for small static files, or if you enable it while using a Tencent Cloud COS origin server and data processing methods such as image processing.
Directions
For instance, you have a video service website that provides online video watching through
video.example.com. The videos are mainly long videos with large files. In order to reduce traffic consumption of large files and improve origin-pull speed, you need to support range requests and origin-pull. You can perform the following steps:1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global site configuration page, then click the Rule Engine tab.
3. On the rule engine management page, click Create rule and select Add blank rule.
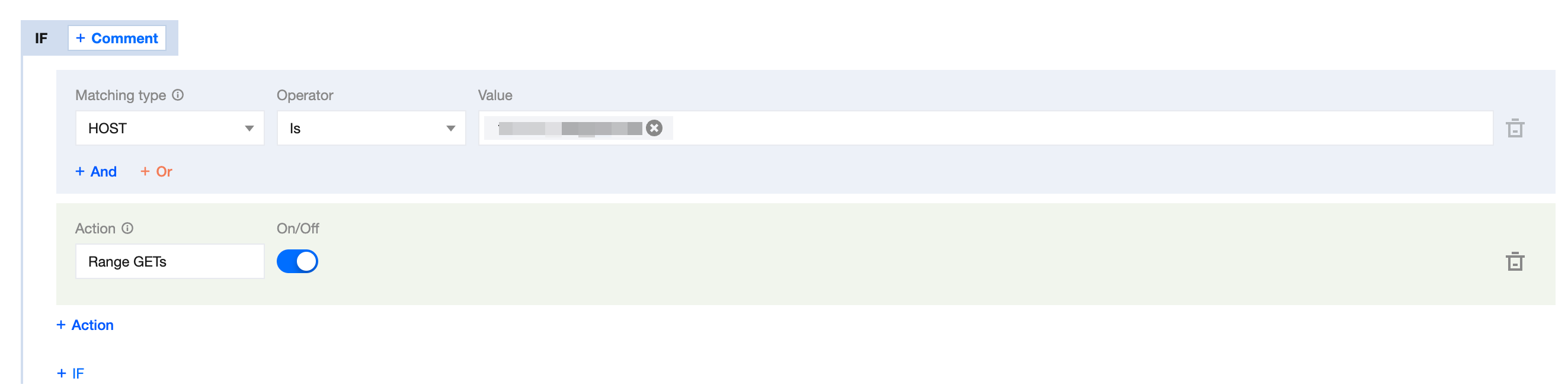
4. On the rule editing page, select the Matching type as
HOST equals video.example.com.5. Click on Action, in the displayed operation list, choose the operation as Range GETs.
6. Click on On/Off to enable Range GETs.
7. Click on Save and publish to complete the configuration of this rule.