CORS Response Configuration
Overview
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is an HTTP header-based mechanism that allows a server to indicate origins (domains, protocols, or ports) other than its own, enabling browsers to permit these origins to access and load their own resources. Currently, many HTML pages load resources such as CSS stylesheets, images, and scripts from different domains. Therefore, addressing cross-domain issues is particularly important.
The CORS standard makes the server declare which sources can use browser to access resources on the server by adding new HTTP response headers.
Cross-Origin Response Headers
Header Field | Description |
Access-Control-Allow-Origin | Values support constants and variables. Among them: Constant: support input *, multiple domain names, IPs, or a mix of domain names and IPs (must contain http:// or https://, such as http://test.com,http://1.1.1.1. Multi-values can be separated by English commas, and up to 1000 characters can be entered.Variable: Match the required cross-origin originating domain via the Origin request header, using the header value ${http.request.headers["Origin"]}. |
Access-Control-Allow-Methods | Used to set the allowed HTTP request methods for cross-origin, you can simultaneously set multiple methods, such as POST, GET, OPTIONS. Multi-values can be separated by English commas, and up to 1000 characters can be entered. |
Access-Control-Max-Age | Used to specify the valid time of preflight request, unit: Seconds, support input 0 ~ 2147483647 integer values.For non-simple cross-origin requests, an additional HTTP query request, called a "pre-request," is required before formal communication to determine whether the cross-origin request is safe and acceptable. The following requests are deemed non-simple cross-origin requests: - Requests initiated via methods other than GET, HEAD, or POST - POST requests with data types other than application/x-www-form-urlencoded, multipart/form-data, or text/plain, such as application/xml or text/xml - Requests using custom request headers, such as Access-Control-Max-Age: 1728000, indicating that no additional pre-request is needed for cross-origin access to the resource within 1728000 seconds. |
Note:
If you set cross-origin response headers on EdgeOne, the response
Access-Control-Allow-Origin header requires that the client request carries the Origin header and this header exactly matches any value set in Access-Control-Allow-Origin.If the origin server has set a cross-origin response header and EdgeOne adds a cross-origin response header simultaneously, two response headers will appear, which will cause a cross-origin error. Additionally, if cross-origin responses are handled by the origin server, the origin response must include the
Vary: Origin header, and the vary feature must be enabled on EdgeOne.Configuration Example
Scenario One: CORS Header Response Only Allows Access to Specified Domain Page Resources
If your business scenario involves cross-domain access, currently the resources of the business domain
www.example.com only allow page access acceleration domains from example.com, site.com. See the steps below.1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration > Rule Engine to open the Rule Engine page.
3. On the rule engine page, click Create Rule and select Add Blank Rule.
4. On the Rule Editing Page, set the match type to HOST equal
www.example.com.Set both the match type and the HTTP request header Origin Header Value equal to
*.example.com, *.site.com.5. Click Operation > Selection Box, and in the pop-up operation list, select the operation as Modify HTTP Node Response Header.
6. Select type as Set, header name as
Access-Control-Allow-Origin, and header value set to ${http.request.headers["Origin"]}.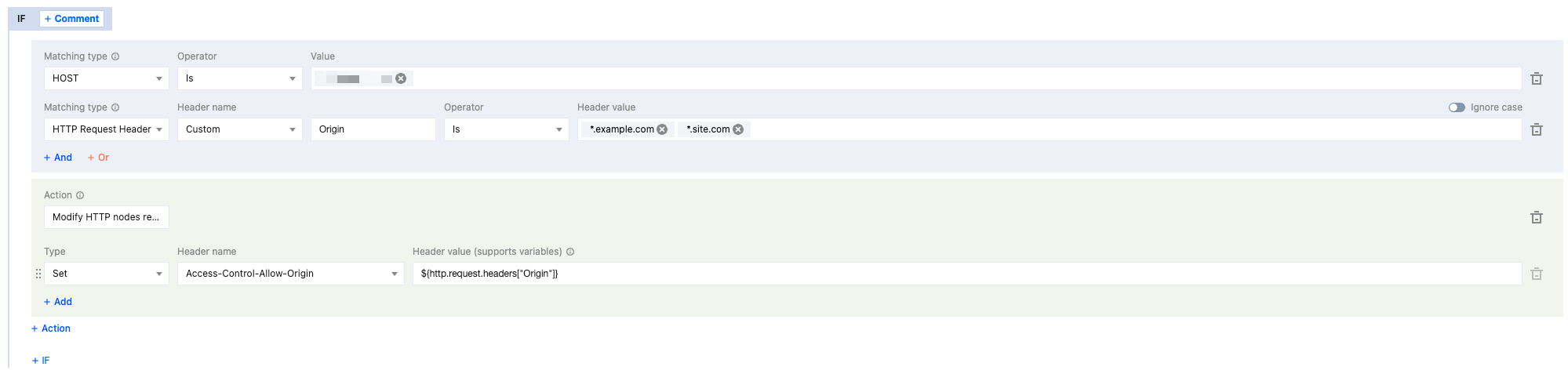
7. Click Save and Publish to complete the configuration.
8. Behavior description takes effect.
When the client request carries Origin:
http://www.example.com, EdgeOne will respond with Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.example.com.When the client request carries Origin:
http://www.site.com, EdgeOne will respond with Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.site.com.When the client request carries Origin:
http://www.abc.com, EdgeOne will not respond with the cross-origin response header Access-Control-Allow-Origin.When the client request does not carry Origin, EdgeOne will not respond with the cross-origin response header
Access-Control-Allow-Origin.Scenario Two: CORS Header Response Supports All Domain Name Access to Page Resources
If your business scenario involves cross-domain access, currently the resources of the business domain
www.example.com allow all page access acceleration domains. See the steps below.1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration > Rule Engine to open the Rule Engine page.
3. On the rule engine page, click Create Rule and select Add Blank Rule.
4. On the Rule Editing Page, set the match type to HOST equal
www.example.com.5. Click Operation > Selection Box, and in the pop-up operation list, select the operation as Modify HTTP Node Response Header.
6. Select type as Set, header name as
Access-Control-Allow-Origin, and header value set to *.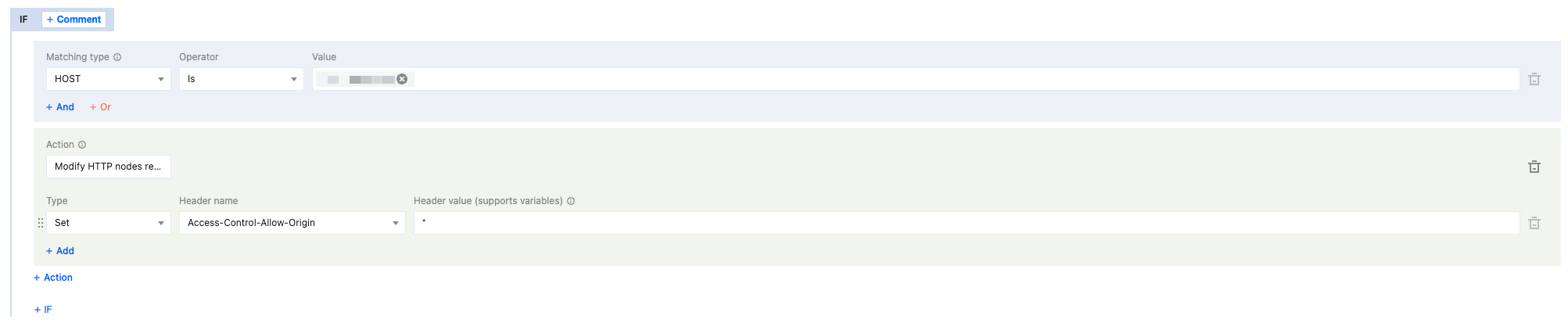
7. Click Save and Publish to complete the configuration.
8. Behavior description takes effect.
When the client request carries
Origin, EdgeOne will respond with Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *.When the client request does not carry
Origin, EdgeOne will not respond with the cross-origin response header Access-Control-Allow-Origin.