Batch Redirect
This example captures incoming HTTP requests and automatically redirects specified paths to corresponding URLs through a predefined redirect mapping table. It can be used for website migration or custom processing of error pages.
Sample Code
// Add a fetch event listener, which is triggered when a request is incoming. It uses the handleRequest function to handle requests and return responses.async function handleRequest(request) {// Define the target external host name.const yourExternalHostname = "www.example.com";// Create mapping from paths to redirect URLs.const redirectMap = new Map([["/foo", "https://" + yourExternalHostname + "/redirect1"],["/bar", "https://" + yourExternalHostname + "/redirect2"],["/baz", "https://" + yourExternalHostname + "/redirect3"],]);// Parse the request URL.const url = new URL(request.url);// Get the path part of the URL.const path = url.pathname;// Check whether the path is in the redirect mapping, and if so, perform a redirect.if (redirectMap.has(path)) {return Response.redirect(redirectMap.get(path), 301);} else {// If the path is not in the mapping, return a 404 status code.return new Response('Not Found', { status: 404 });}}// When a request event occurs, use the handleRequest function to handle it.addEventListener('fetch', event => {event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request));});
Sample Preview
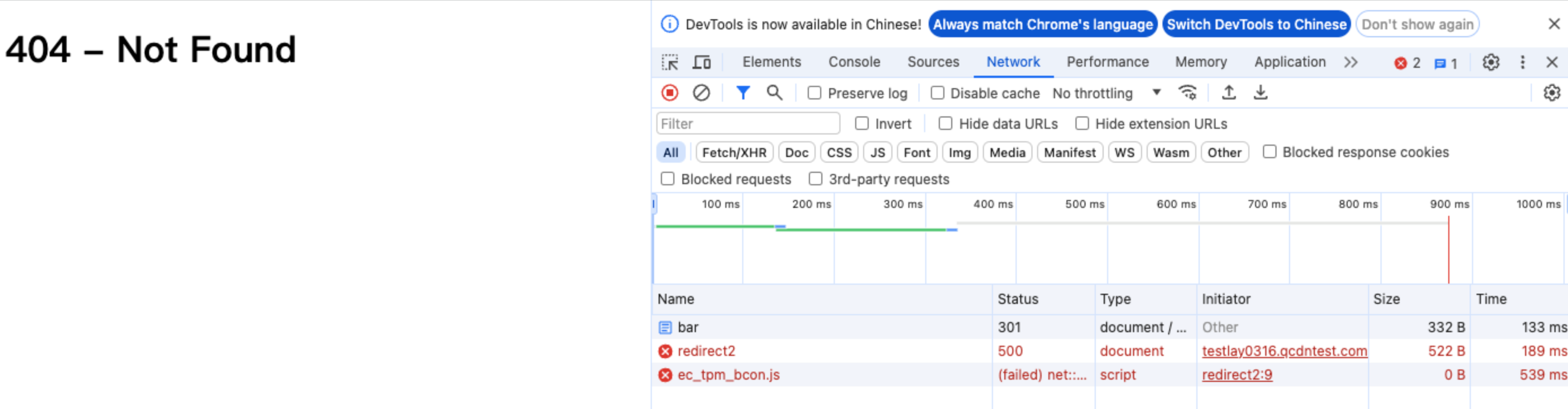
In the address bar of the browser, enter a URL that matches a triggering rule of the edge function. If the path contains /bar, a 301 redirect to
https://www.example.com/redirect2 will be performed automatically.The preview is as follows. 404 is shown currently. Because no resources exist under the target host name www.example.com and the path /redirect2, you should replace the target host name and path with actual values.
Related References