Verify Business Access
After your domain is connected to EdgeOne, you need to switch DNS resolution and add the CNAME record assigned by EdgeOne to make the service effective. Before performing this operation, it is recommended to fully test and verify to ensure that your business can be accessed normally after the switch. This document will guide you on how to perform verification.
For example, if your current acceleration domain name is
www.example.com, the verification steps after access are as follows:1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the left sidebar, click Domain Name Service > Domain Management.
3. In the Domain Management page, if you have already added a domain, you can see the CNAME address allocated by EdgeOne for that domain.
For example:
www.example.com.eo.dnse5.com.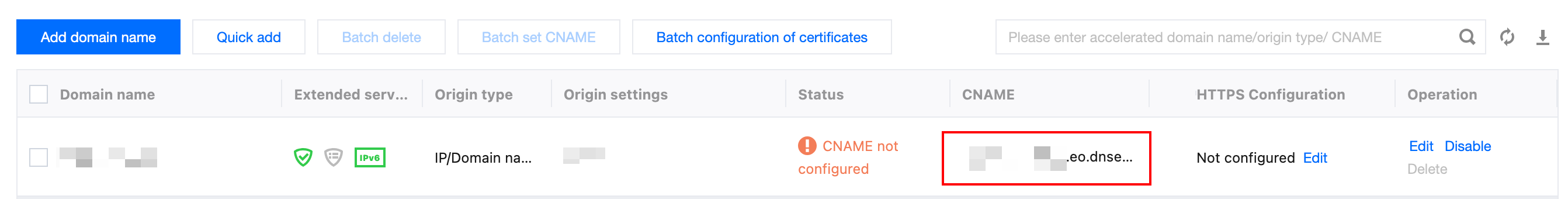
4. Use the TCCLI (CMD running tool or terminal) and the
nslookup command to get the edge IP resolved from the above CNAME. For example, nslookup www.example.com.eo.dnse5.com. The obtained IPs, such as 59.56.100.101 or 175.6.193.206, are EdgeOne edge node IPs.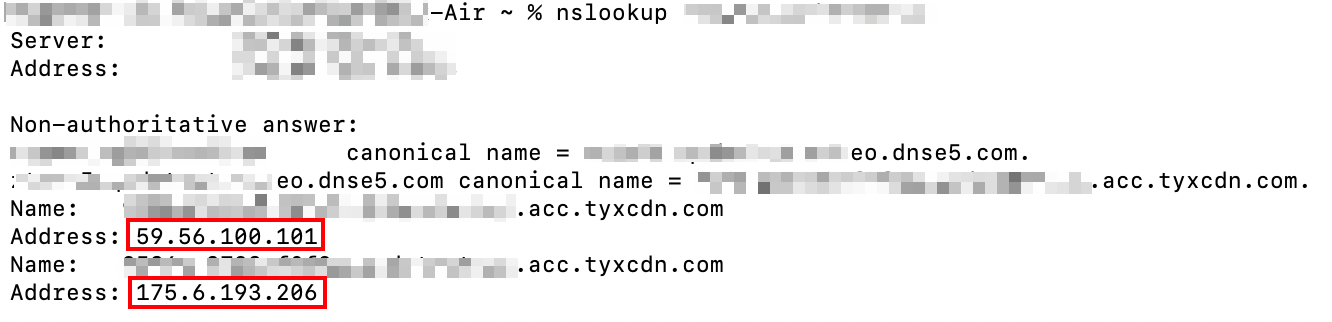
5. You can continue to refer to the following two methods for verification:
Depending on your operating system, you can refer to the following methods to bind the host for testing verification:
Find the hosts file in the system and bind the IP address to your acceleration domain name. Bind any node IP ( 27.152.181.195 ) obtained in step 4 and the acceleration domain name (
www.example.com ) to the local hosts file on your computer. The format should be the IP address followed by the acceleration domain name, with a space between them, as shown below: Note:
The directory of the hosts file in the Windows system is:
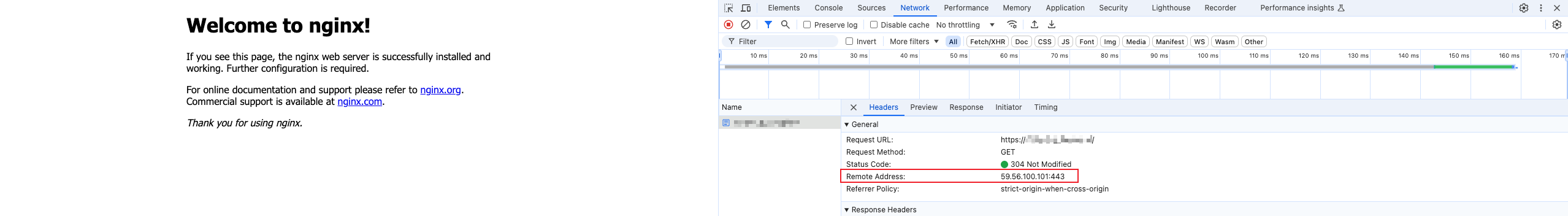
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc . If you do not have the permission to edit the file in this directory, you can copy the file, edit the copy, and then replace the original file with the edited copy.After completing and saving the configuration, perform a business access test through the browser. Directly access the test URL of the current acceleration domain name, open the browser's developer tools, and check whether the accessed IP is the currently bound edge node IP. At the same time, check whether the access performance meets your expectations.
Find the hosts file in the system and bind the IP address to your acceleration domain name. Bind any node IP ( 27.152.181.195 ) obtained in step 4 and the acceleration domain name (
www.example.com ) to the local hosts file on your computer. The format should be the IP address followed by the acceleration domain name, with a space between them, as shown below: Note:
The directory of the hosts file in the Mac system is:
/etc/ . If you do not have permission to edit the file in this directory, you can copy the file, edit the copy, and then replace the original file with the edited copy.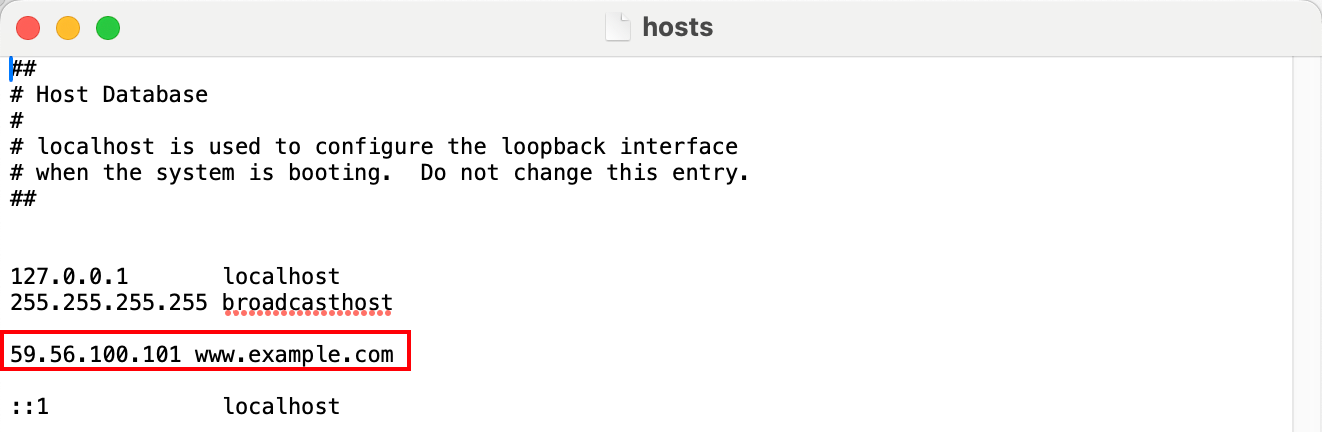
After completing and saving the configuration, perform a business access test through the browser. Directly access the test URL of the current acceleration domain name, open the browser's developer tools, and check whether the accessed IP is the currently bound edge node IP. At the same time, check whether the access performance meets your expectations.
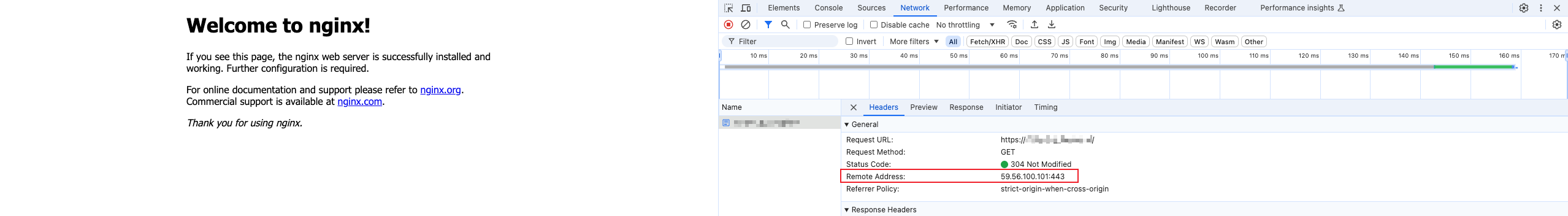
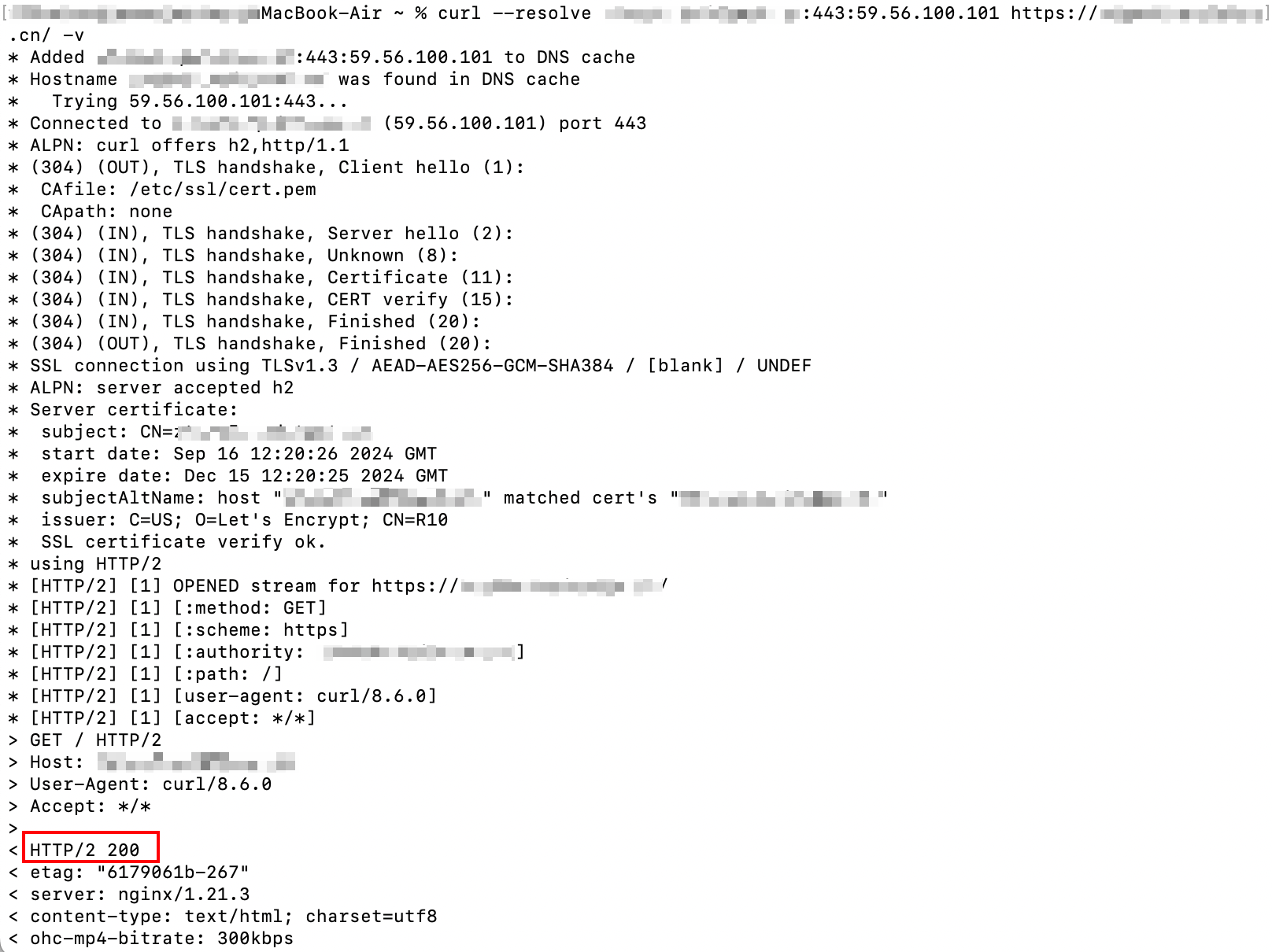
You can refer to the following curl command.
curl --resolve <hostname>:<port>:<ip> <url> -v
The hostname is the domain name you need to access, such as
www.example.com . The port is the specified port number for access, which is port 443 for HTTPS access and port 80 for HTTP access. The ip is the IP address obtained in step 4, and the url is the URL used for the current access test. For example: curl --resolve www.example.com:443:59.56.100.101 https://www.example.com/ -v .Check whether the request result is normal and meets your expectations.
6. Once the access is verified to meet expectations, you can switch your domain name resolution to the EdgeOne Service. For details, refer to: Modify CNAME resolution.