Action
The Web protection module provides multiple action options. Different feature modules support different actions, please refer to the specific feature module document.
Action | Use Case | Action Description | Subsequent Action |
Block | Used to block requests to access a site (including cached or non-cached content). | Respond with block page and block status code. | No longer matches other policies |
Allow | Used to skip the remaining rules in the current security module. | In the current module, the remaining rules will no longer match this request. | Continue to match other effective rules |
Monitor | Used to evaluate or grayscale its security policies. | Logs are only recorded, no actions are taken. | Continue to match other rules |
Redirect | Used to provide standby resources and improve user access experience when blocked. | Redirect to the specified URL. | No longer matches other policies |
ReturnCustomPage | Used to provide block pages with a better experience. Used to be compatible with the API format and respond to error messages that the API can parse. Used to monitor business and monitor blocked requests by specifying status codes. | Returns a custom error page and status code. Supports referencing page content defined in the Custom Error Page feature. | No longer matches other policies |
BlockIP | Used to punish malicious clients. | When a request matches the conditions, discard requests from that client IP within a period of time. Note: If the matching condition used is client IP (the XFF header is matched first), IP blocking will be based on the request source client IP, rather than the XFF header. Configure with caution. | No longer matches other policies |
JSChallenge | Used to identify tool clients that do not support JavaScript, frequently seen in DDoS attack sources. | Respond with an HTTP 302 redirect page, the page carries JavaScript code to verify the client browser behavior, and only the visitors that passes the verification can continue to access. | Requests that pass the challenge continue to match other rules |
ManagedChallenge | Used for Bot defense, JavaScript challenge verification is first performed, and then CAPTCHA human verification is performed on requests that pass the verification. | First take the JavaScript challenge. For clients that pass the verification, they need to respond to the redirection (HTTP 302) page and carry the verification code for verification, and the user completes the verification through interactive operations. Only visitors who pass both verifications can continue to visit. | Requests that pass the challenge continue to match other rules |
JavaScript Challenge
The JavaScript challenge verification process is imperceptible browser verification, neither displaying a verification page nor requiring manual intervention. The browser can automatically complete the verification and display the requested resources. This method can effectively filter DDoS attacks initiated by distributed scripts.
JavaScript Challenge Use Cases
JavaScript Challenge mainly applies to protection of the following resources:
Pages visited in the browser;
Resources accessed only after you visit a page in the browser.
Note:
JavaScript Challenge is not suitable for the following scenarios:
Non-browser client access and certain scenarios, such as APIs accessed by mobile applications and APIs not called through a page. In such scenarios, the client may fail to pass verification for it cannot handle the JavaScript response content properly, thereby causing access to be blocked.
Scenarios where the request header options such as Accept are used for accessing non-HTML static resources. In such scenarios, the client may fail to pass verification for the JavaScript challenge response content does not match the Content-Type option in the Accept header, thereby causing failure of the resource access.
For the above business scenarios, you should use the ReturnCustomPage , Redirect or Block action, or configure protection exception rules to ensure normal business operation.
JavaScript Challenge Interaction Flow
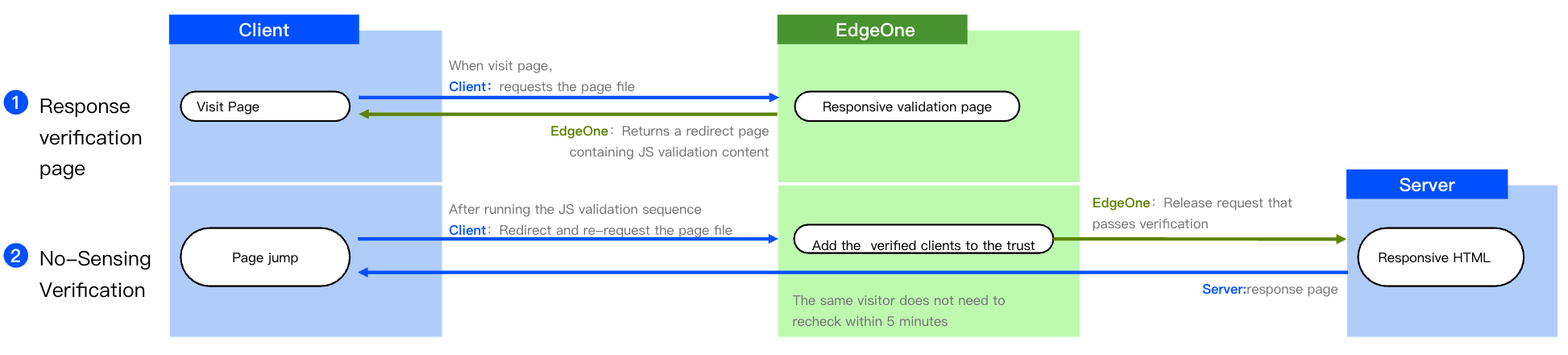
When the security policy uses JavaScript Challenge to handle requests, EdgeOne responds with a redirect page (HTTP 302) containing a JavaScript program to verify the browser runtime environment. After receiving this response, browsers with JavaScript enabled will execute the verification program and perform an HTTP 302 redirect. After receiving the redirect request, the EdgeOne security protection module will allow requests carrying valid identifiers (client IP and User-Agent).
Managed Challenge
Managed Challenge integrates JavaScript Challenge and CAPTCHA (human-machine verification) to verify the browser environment and human users through two-factor authentication. This method effectively filters out non-browser client access.
Managed Challenge Interaction Flow
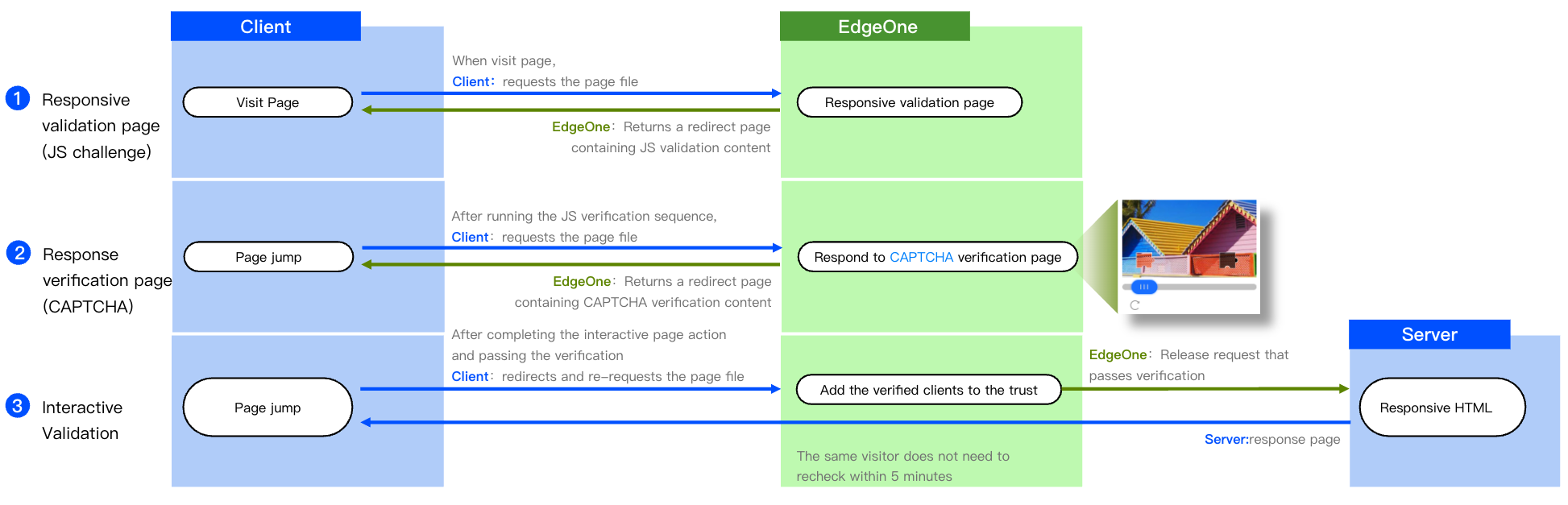
When the security protection policy uses JavaScript Challenge to handle requests, EdgeOne first implements the JavaScript challenge mechanism, that is, responds with a redirect page (HTTP 302) containing a JavaScript program to verify the browser runtime environment. After receiving this response, browsers with JavaScript enabled will continue to respond with a redirect page (HTTP 302) that has an embedded interactive CAPTCHA verification program. After the program completes verification on the client, an HTTP 302 redirect is performed. After receiving the redirect request, the EdgeOne security protection module will allow requests carrying valid identifiers (client IP and User-Agent).
Note:
When the client frequently attempts JavaScript challenges and triggers interceptions, it will lead to the client entering the JavaScript Challenge blocklist. For a period of time, the security policy will no longer respond to JS challenges for that client and will directly respond with an interception page. To restore the client's access, please configure Protection Exception Rules.