Configuring DNS Records
This document describes how to configure the DNS record on EdgeOne.
Note:
This feature is only available for sites connected via the NS.
Prerequisite
1. Connect your site to EdgeOne via NS.
2. Modify the DNS server of your domain to the DNS server provided by EdgeOne. For details, see Modifying DNS Server.
Adding one DNS Record
1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. In the left sidebar, click Domain Name Service > DNS Records.
3. On the DNS Record page, click Add record, complete the parameters, and click Save. For a description of related parameters, refer to: Description of DNS-related Concepts.
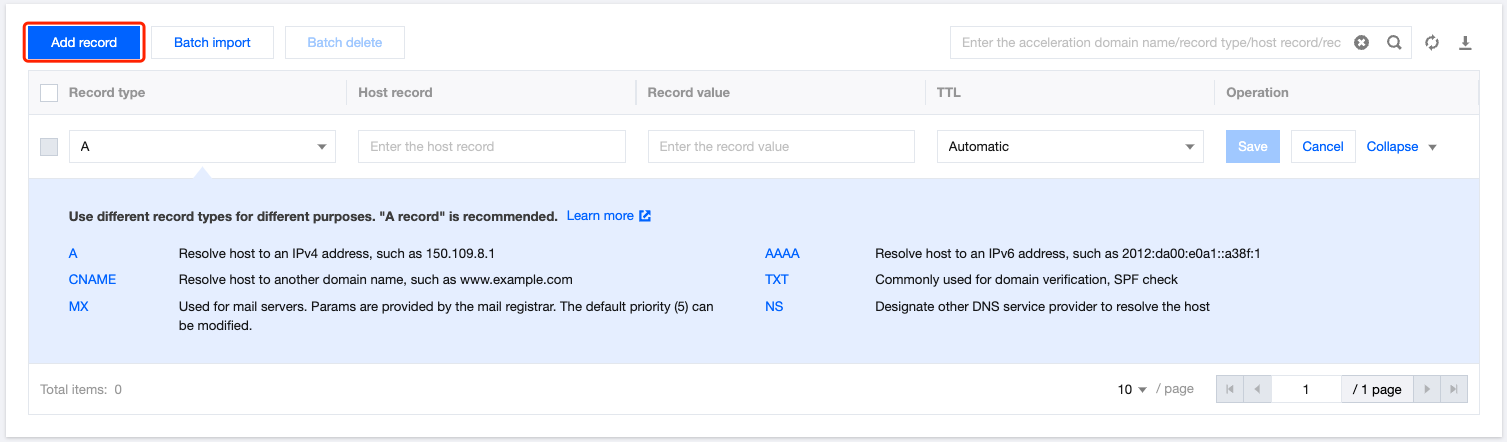
Note:
After a DNS record is added, it only provides DNS resolution capabilities. If you want the domain name to be connected to EdgeOne for security acceleration, click Add as Accelerated Domain Name in the action column, and refer to the Adding an Accelerated Domain Name document to connect the domain name to EdgeOne.
Description of DNS-related Concepts
Host Record
The host record is equivalent to the subdomain name's prefix, and is used to map the domain name to a specific IP address or other related information. When you enter a URL in your browser, your device will query the DNS server to obtain the IP address corresponding to the URL. This process is completed by looking up the DNS record. For example, if your current site is
example.com and the domain name you want to connect is www.example.com , www will be input as the host record.Description of Resolution Record Types
Record Type | Description | Example |
A | It is used to resolve a domain name to an IPv4 address. The record value only allows the input of an address in the IPv4 format and does not permit the use of a private IP address. | For example, you have a domain name example.com , and its A record is 1.1.1.1 . When users visit example.com , the DNS will resolve it to the IP address. |
AAAA | It is used to resolve a domain name to an IPv6 address. The record value only allows the input of an address in the IPv6 format and does not permit the use of a private IP address. | For example, you have a domain name example.com , and its AAAA record is 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 . When users visit example.com , the DNS will resolve it to the IP address, allowing users to access the website via IPv6. |
CNAME | It is used to point a domain name alias to another domain name. The record value only allows the input of a domain name. | For example, you have a subdomain name www.example.com , and its CNAME record points to example.com . When users visit www.example.com , they will be redirected to example.com to obtain the corresponding resolution record result. |
MX | It is used to specify a mail server for handling emails. The MX record must include the priority and the server address, where: Priority: The input range allowed is 0-50; Mail server address: Only a domain name is allowed. | If you want to forward emails sent to example.com to a mail server, you can set an MX record, such as 10 mail.example.com , where 10 is the priority number, with a lower number indicating a higher priority. |
TXT | It is used to store any text information, often for verification and security purposes. The record value must not exceed 256 bytes. | Common uses include sender policy framework (SPF) recording and domain name validation. For example, you can configure a TXT record v=spf1 include:_spf.example.com ~all to specify which servers are allowed to send emails on behalf of your domain name. |
NS | It is used to specify the DNS server responsible for managing the domain name. The record value must be in the domain name format. | For example, you have a domain name example.com , and its NS record may be ns1.example.com and ns2.example.com , indicating that these DNS servers are responsible for authoritative DNS queries for the domain name. |
SRV | It is used to define the hostname and port number of a specific service. The record value should include the corresponding host domain name and port number. | If you have a service (such as VoIP or instant messaging), you can use an SRV record to specify the service's hostname and port. For example: _sip._tcp.example.com may point to port 5060 of sipserver.example.com . |
CAA | It is used to specify which certificate authorities (CAs) are authorized to issue SSL/TLS certificates for domain names. The record value format needs to include three pieces of information: flag, tag, and value, separated by spaces: Flag: It must be set to 0, indicating that CAs are allowed to issue certificates for domain names even if they cannot recognize the CAA record attribute. Tag: It is usually "issue", "issuewild", or "iodef": issue: The specified CA is allowed to issue certificates for all subdomain names. issuewild: The specified CA is allowed to issue wildcard certificates for all subdomain names. iodef: A URL is provided, so that the CA can send a report to it when encountering a request that violates the CAA policy. Value: string type. It is usually the domain name of the CA allowed to issue certificates, and needs to be enclosed in double quotes. | You can set a CAA record so that only specific CAs can issue certificates for your domain name. For example: 0 issue "letsencrypt.org" , indicating that only Let's Encrypt can issue certificates for the domain name. |
Description of Resolution Record Conflicts
When recursive resolution queries are performed, there is priority among record types. For example, according to RFC1034 and RFC2181, CNAME has the highest priority. Therefore, the CNAME resolution record result will be returned first in the resolution requesting process. As a result, if a CNAME record is set, it is not allowed to configure MX and TXT records to prevent record conflicts.
✓: No conflict. Both types of resolution records can coexist under the same host record. For example, if an A record for
www.example.com is set, an MX record for www.example.com can also be set.×: Conflict. Both types of resolution records cannot coexist under the same host record. For example, if an A record for
www.example.com is set, a CNAME record for www.example.com cannot be set.Record Type | A | AAAA | CNAME | MX | NS | TXT | SRV | CAA |
A | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
AAAA | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
CNAME | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | × |
MX | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
NS | × | × | × | × | ✓ | × | × | × |
TXT | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
SRV | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
CAA | ✓ | ✓ | × | ✓ | × | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Note:
The above table shows conflicts when the host record is not @. When the host record is @, CNAME records do not conflict with MX and TXT records, and configuration is allowed. However, conflicts in resolution records may still occur. For conflict details and risks, refer to: Description of Conflicts between CNAME and MX, TXT Records.
Weight Description
The weight allows you to set different record values for the same host record, record type, and resolution route. During resolution, EdgeOne will randomly return the corresponding resolution result according to the weight ratio.
Only A/AAAA/CNAME records allow weight configuration. The default weight is empty, meaning no weight is configured. The input range is 0-100. When the weight is set to 0, it means no resolution, but it is not allowed to set all weights to 0. If there are multiple resolution records with the same name after the weight is configured, the resolution record result will be returned according to the weight. The calculation method for the weight is: ultimately effective weight = weight of current record / sum of weights of all records with the same name .
Below is an example:
Suppose there are currently 3 CNAME records with the same host record name: Record A, Record B, and Record C, with the weight set to 0, 60, and 40 respectively. The final weight effectiveness result is that Record A is not resolved, Record B's weight ratio is: 60/(60 + 40) = 60%, and Record C's weight ratio is: 40/(60 + 40) = 40%.
Note:
Up to 15 A/AAAA/CNAME records for the same host record can be added simultaneously.
If there are multiple A/AAAA/CNAME records for the same host record name and the weights are configured, the weight switches for all records must be consistent, that is, the weights must be all configured or all disabled.
Description of Resolution Route
By default, when DNS resolution is requested, the authoritative server will not determine the user's IP source to return the resolution record value. EdgeOne supports resolution route allocation, and can return the corresponding route's resolution record value based on the resolution route to which the user's request IP belongs during resolution. If you want to return different resolution records based on the user's IP region source, you can configure different record values according to the region. For example: for the current domain name
www.example.com , if the A record for the Chinese mainland region route is configured to resolution to 1.1.1.1 and the A record for the default route is configured to resolution to 2.2.2.2 , then users from the Chinese mainland will have the domain name www.example.com resolved to 1.1.1.1 , whereas users from other regions will have it resolved to 2.2.2.2 . Note:
This feature is supported only by Standard and Enterprise plans.
Currently, only A/AAAA/CNAME records support the configuration of resolution routes, with a maximum of 15 resolution routes configurable for the same host record.
TTL
TTL (Time To Live) indicates the caching duration (in seconds) of DNS records on DNS servers at all levels. When the TTL of a DNS record expires, the Local DNS server needs to request the authoritative DNS server to obtain the resolution of the record again to ensure the DNS record information is up to date. The shorter the set TTL, the more frequently you will need to request the authoritative server to resolve the record, which may slightly affect resolution performance. If the set TTL is long, it may affect the actual effective time of the record when there is a record update. The TTL of EdgeOne is set to 5 minutes by default, and you can modify it based on your actual business needs.