Caching POST Requests
In this example, an SHA-256 signature is calculated for the request body of a POST request and used as a part of the cache key, and the Cache API is called to cache the response content. If the content is already stored in the cache, the cached content is sent to the client. Otherwise, the Fetch API is called to initiate a subrequest to fetch a remote resource. This example demonstrates how to use an edge function to cache POST requests.
Sample Code
function uint8ArrayToHex(arr) {return Array.prototype.map.call(arr, (x) => (('0' + x.toString(16)).slice(-2))).join('');}// The SHA-256 signature digest.async function sha256(message) {const msgBuffer = new TextEncoder().encode(message);const hashBuffer = await crypto.subtle.digest('SHA-256', msgBuffer);return uint8ArrayToHex(new Uint8Array(hashBuffer));}async function fetchContent(event, cacheKey) {const cache = caches.default;// If the resource is not found in the cache, fetch the resource from the origin server and cache the resource.const response = await fetch(event.request);// Add the Cache-Control field to the response header and specify the cache duration.response.headers.set('Cache-Control', 's-maxage=10');event.waitUntil(cache.put(cacheKey, response.clone()));// Add an identifier indicating that the resource is not found in the cache to the response header.response.headers.append('x-edgefunctions-cache', 'miss');return response;}async function handleRequest(event) {const request = event.request;const body = await request.clone().text();// // Calculate the hash value based on the request body.const hash = await sha256(body);// Use the hash value that is calculated based on the request body as a part of the cache key.const cacheKey = `${request.url}${hash}`;const cache = caches.default;try {// Fetch the associated response content from the cache.let response = await cache.match(cacheKey);if (!response) {return fetchContent(event, cacheKey);}// Add an identifier indicating that the resource is found in the cache to the response header.response.headers.append('x-edgefunctions-cache', 'hit');return response;} catch (error) {await cache.delete(cacheKey);// If the cache duration of the resource times out or the resource is not found in the cache, re-fetch the remote resource.return fetchContent(event, cacheKey);}return response;}addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {try {const request = event.request;// Process a POST request.if (request.method.toUpperCase() === 'POST') {return event.respondWith(handleRequest(event));}// Non-POST request.return event.respondWith(fetch(request));} catch (e) {return event.respondWith(new Response('Error thrown ' + e.message));}});
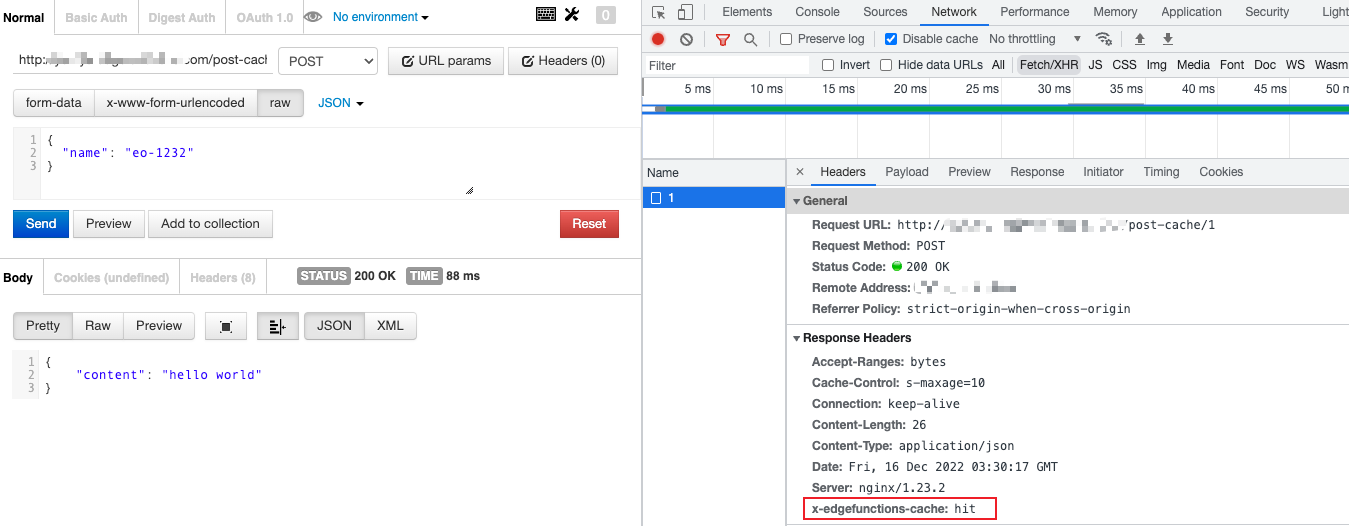
Sample Preview
In the address bar of the browser, enter a URL that matches a trigger rule of the edge function to preview the effect of the sample code.
The resource is not found in the cache.

The resource is found in the cache.