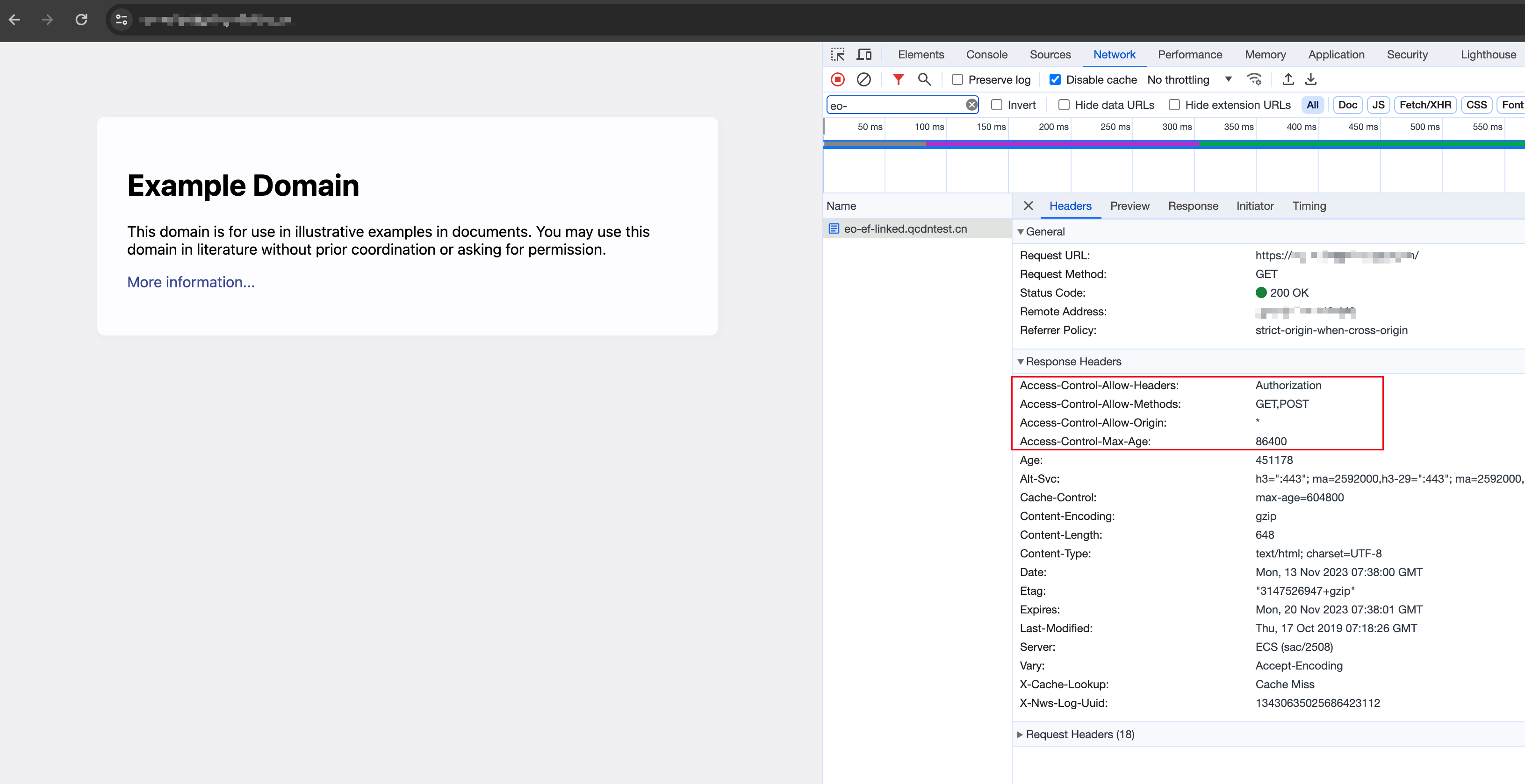
Modifying a Response Header
This example uses the Fetch API to implement a reverse proxy for the domain name www.example.com of the site, and sets the HTTP response headers through Edge functions to achieve CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing).
Sample Code
async function handleRequest(event) {const { request } = event;const urlInfo = new URL(request.url);const proxyRequest = new Request(`https://www.example.com${urlInfo.pathname}${urlInfo.search}`, {method: request.method,body: request.body,headers: request.headers,copyHeaders: true,});proxyRequest.headers.set('Host', 'www.example.com');// fetch reverse proxyconst response = await fetch(proxyRequest);/** Add custom response headers **/// Specify which origins are allowed to access resourcesresponse.headers.append('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');// Specify which HTTP methods (such as GET, POST, etc.) are allowed to access resourcesresponse.headers.append('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET,POST');// Specify which HTTP headers can appear in the request headerresponse.headers.append('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Authorization');// How long the result of the pre-flight request can be cachedresponse.headers.append('Access-Control-Max-Age', '86400');/** Delete response headers **/response.headers.delete('X-Cache');return response;}addEventListener('fetch', event => {event.respondWith(handleRequest(event));});
Sample Preview
In the address bar of the browser, enter a URL that matches a trigger rule of the edge function to preview the effect of the sample code.