Modifying HTTP Response Headers
Overview
Support customization/adding/deleting HTTP node response headers (responding to the customer's direction), modifying HTTP node response headers will not affect the node cache.
Note:
EdgeOne has automatically carried some response headers by default, and you don't need to configure them. For details, please refer to: Default HTTP Response Headers.
Scenario 1: Cross-Domain Header Response Only Allows Specified Domain Names to Access Page Resources
If your business scenario involves cross-domain access and the resources of the current business domain name
www.example.com only allow the pages from example.com and site.com to access the acceleration domain name, you can refer to the following steps.1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global configuration page. Then click the Rule Engine tab.
3. On the rule engine page, click Create rule and select Add blank rule.
4. On the rule editing page, select the matching type as HOST equals
www.example.com.At the same time, select the matching type as HTTP request header Origin equals
*.example.com and *.site.com.5. Click the Action checkbox and select Modify HTTP nodes response header in the pop-up operation list.
6. Select the type as Set and the header name as
Access-Control-Allow-Origin, and set the header value to ${http.request.headers["Origin"]}.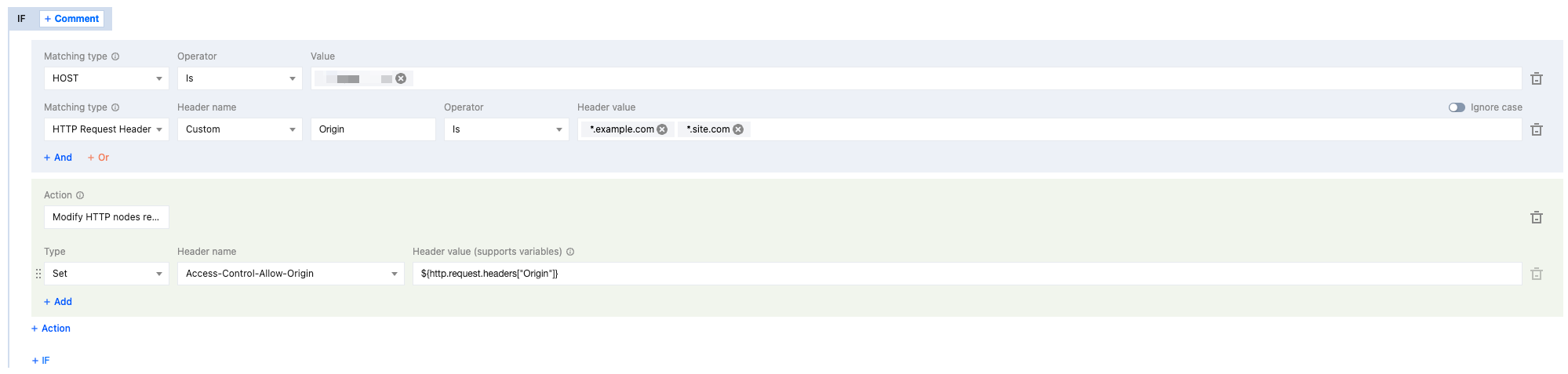
7. Click Save and publish to complete the rule configuration.
Scenario 2: Cross-Domain Header Response Supports All Domain Names to Access Page Resources
If your business scenario involves cross-domain access and the resources of the current business domain name
www.example.com allow all pages to access the acceleration domain name, you can refer to the following steps.1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global configuration page. Then click the Rule Engine tab.
3. On the rule engine page, click Create rule and select Add blank rule.
4. On the rule editing page, select the matching type as HOST equals
www.example.com.5. Click the Action, and in the pop-up operation list, select the operation to modify the HTTP node response header.
6. Select the type as set, and set the
Access-Control-Allow-Origin as * .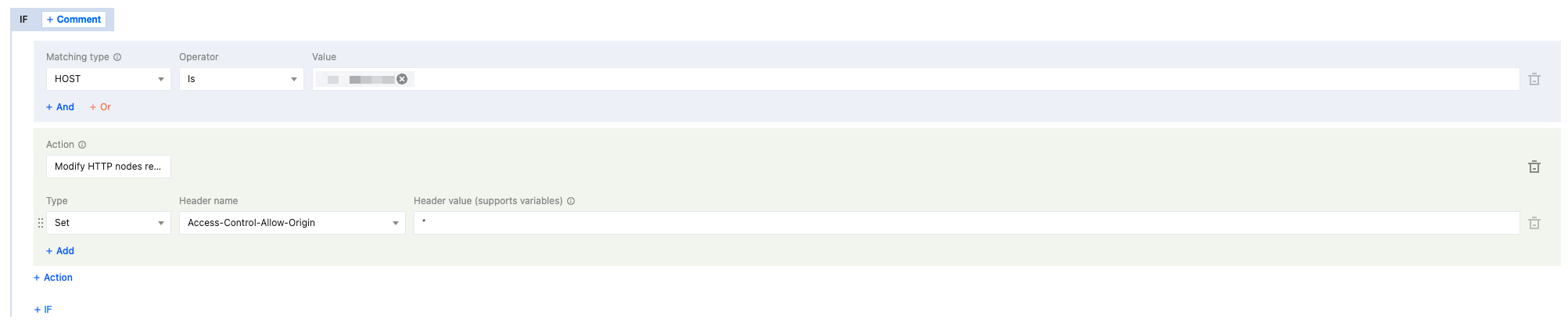
7. Click Save and publish to complete the rule configuration.
Related References
Supported Types Description:
Type | Description |
Set | Change the value of the specified header parameter to the set value, and the header is unique. Note: If the specified header does not exist, the header will be added. |
Add | Add the specified header. Note: If the header already exists, it will still be added and will not overwrite the existing header. |
Delete | Delete the specified header. |
Supported Header Types Description:
Header Type | Description |
Custom | Supports modifying custom header content, fill in the description as follows: Name: 1 - 100 characters, consisting of numbers 0 - 9, characters a - z, A - Z, and special symbols -. Value: Supports 1 - 1000 characters, does not support Chinese. |
Specify Header | Supports modifying the following specified headers: Access-Control-Allow-Origin: Used to specify the source (domain name) allowed to access resources, must contain http:// or https://. Supports setting Wildcard * , i.e., allowing all domain requests.Access-Control-Allow-Methods: Used to set the HTTP request methods allowed for cross-domain access, such as POST, GET, OPTIONS. Access-Control-Max-Age: Specifies how many seconds the preflight request result is valid, in seconds. Content-Disposition: Activates the browser's download pop-up window and can set the default download file name. For example: Content-Disposition: attachment;filename=FileName.txt Content-Language: Defines the language code used by the page. For example: Content-Language: zh-CN |
Limitations
In the same Modify HTTP Request Header operation, multiple different types of operations can be added, up to 30, and the execution order is from top to bottom.
Some standard headers are not supported for configuration, as follows:
DateCache-Control(Only deletion is not supported)CDN-Loopxx-script-xxxEO-Inner-xxxEO-Cache-StatusEO-LOG-UUIDEO-Debug-xxxContent-LengthContent-Range