Smart Acceleration
Function Introduction
When your site provides dynamic content services or mixed dynamic and static content, the user's request for dynamic content needs an origin-pull request to respond to different resource content according to the user. At this time, due to the differences in the region and operator of the client, the network environment is complex and intricate. When accessing across regions and operators, it may cause slow access requests, high packet loss rates, and other situations for users.
Smart acceleration can adjust and optimize network paths in real-time. After enabling this function, EdgeOne will detect node network latency in real-time, select the best access path through intelligent algorithms, and dynamically adjust resource allocation and utilization according to the real-time network conditions, to help improve user experience and ensure business continuity.
Billing Description
This function is a value-added service. After enabling smart acceleration, the upstream traffic of client users and EdgeOne nodes will be included in the security acceleration traffic fee based on the original billing items, and value-added service fees will be charged according to the number of business requests. For details, please refer to the Billing Overview.
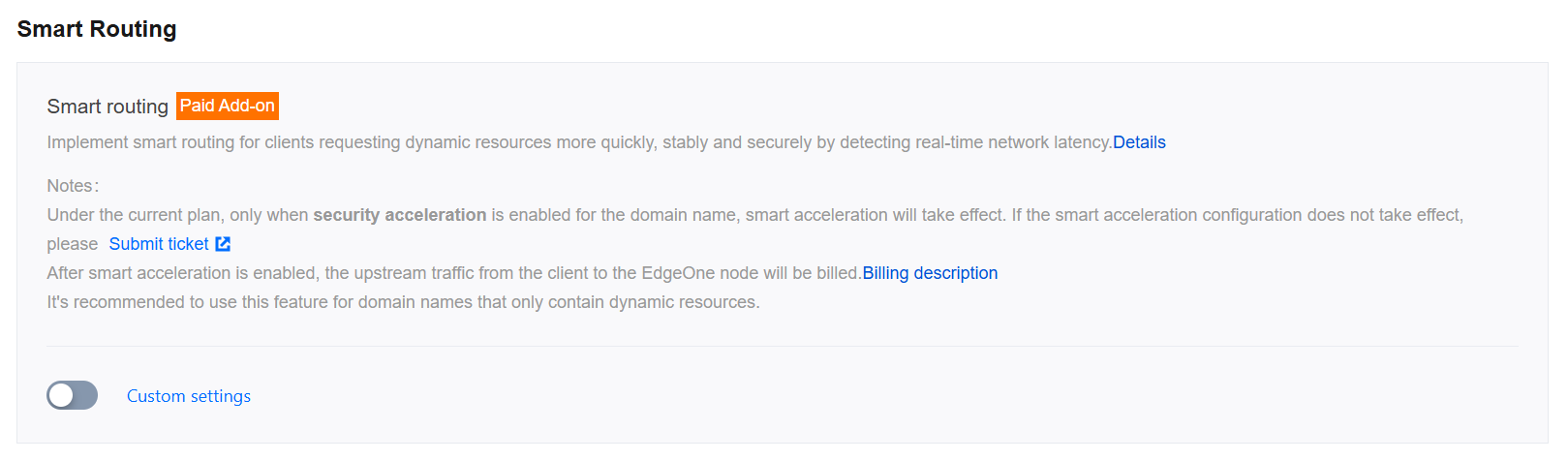
Scenario 1: Enable smart acceleration for all domain names of the site
If your site is all mixed dynamic and static resources or pure dynamic resources, you need to enable smart acceleration for the whole connected site. Please refer to the following steps:
1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global site configuration page.
3. Find the smart acceleration configuration card, which is off by default. Click the switch to configure on/off.
Scenario 2: Enable smart acceleration for specified domain names
If only a certain domain name under your site is pure dynamic resources or mixed dynamic and static resources, you need to enable smart acceleration separately for the specified domain name. Please refer to the following steps:
1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Site Acceleration to enter the global site configuration page. Then click the Rule Engine tab.
3. On the rule engine management page, click Create rule and select Add blank rule.
4. On the rule editing page, select the Host matching type to match the requests of the specified domain name.
5. Click Action > Select Box, and in the pop-up action list, select the action as smart acceleration, and click the switch to turn on/off.

6. Click Save and Publish to complete the rule configuration.
Related Reference
What are static resources and what are dynamic resources?
Static resources: When a user accesses a resource multiple times, the same content is returned. For example: images, videos, software installation packages, compressed files, CSS, JavaScript files, and other content that does not change frequently.
Dynamic resources: When a user accesses a resource multiple times, different content is returned. That is, content that needs real-time updates, user interaction, and other dynamic content. For example: API interfaces,
jsp, asp, php, perl, and cgi format files, etc.